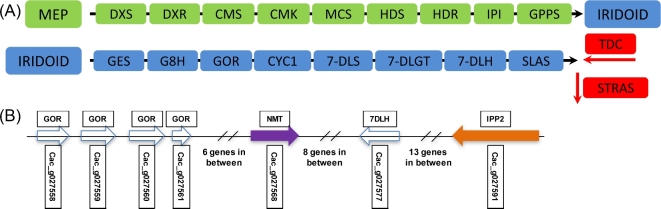
Figure 4:
Key portions of the proposed camptothecin biosynthetic pathway and an example of physical clustering of candidate genes in Camptotheca acuminata. (A) The methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway (green), iridoid pathway (blue), and condensation of secologanic acid with tryptamine via strictosidinic acid synthase (STRAS) to form strictosidinic acid prior to downstream dehydration, reduction, and oxidation steps yielding camptothecin. 7-DLGT: 7-deoxyloganetic acid glucosyltransferase; 7-DLH: 7-deoxyloganic acid hydroxylase; 7-DLS: 7-deoxyloganetic acid synthase; CMK: 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase; CMS: 4-diphosphocytidyl-methylerythritol 2-phosphate synthase; CYC1: iridoid cyclase 1; DXR: 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase; DXS: 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase 2; G8H: geraniol 8-hydroxylase; GES: plastid geraniol synthase; GOR: 8-hydroxygeraniol oxidoreductase; GPPS: geranyl pyrophosphate synthase; HDR: 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-butenyl 4-diphosphate reductase; HDS: GCPE protein; IPI: plastid isopentenyl pyrophosphate, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate isomerase; MCS: 2C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; SLAS: secologanic acid synthase; TDC: tryptophan decarboxylase. (B) Physical clustering of homologs of genes involved in the methylerythritol phosphate, iridoid, and alkaloid biosynthetic pathways of Catharanthus roseus on scaffold 151 of C. acuminata. Gene IDs are below the arrows. 7DLH: 7-deoxyloganic acid 7-hydroxylase; GOR: 8-hydroxygeraniol oxidoreductase; IPP2: isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase II; NMT: 16-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-3-hydroxytabersonine N-methyltransferase.