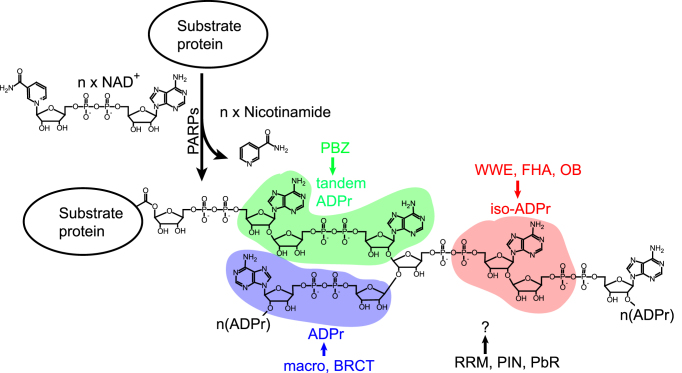
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of PAR synthesis. PARPs hydrolyze nicotinamide from NAD+ and covalently link the remaining ADP-ribose moieties to their substrates, forming linear or branched PAR chains. Different PAR readers recognize distinct units of the PAR chain. The PBZ motif recognizes tandem ADP-ribose. The WWE, FHA and OB domains recognize iso-ADP-ribose. The macro and BRCT domains recognize ADP-ribose. The recognition units of the RRM, PIN and PbR domains need to be identified. ADPr: ADP-ribose; iso-ADPr: iso-ADP-ribose.