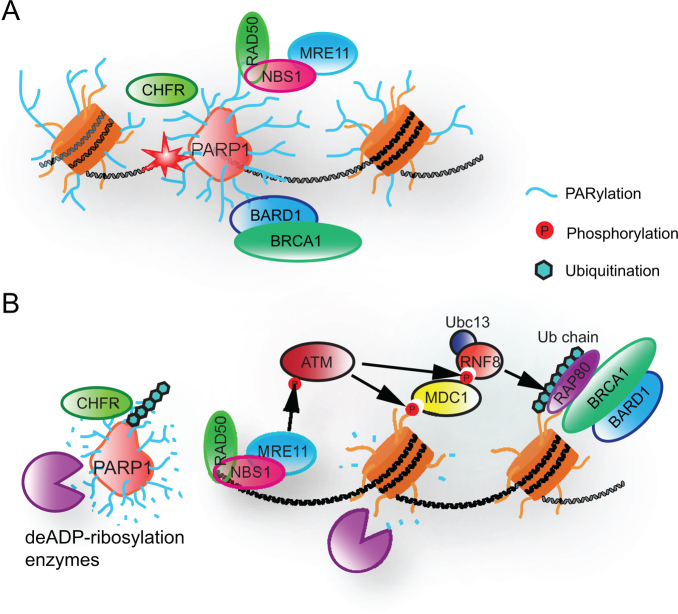
Figure 5.
Functional interactions between DNA damage-induced PARylation and other post-translational modifications. (A) PARP1-mediated PARylation facilitates the early recruitment of DNA damage factors (e.g. NBS1, BARD1 and CHFR). (B) In response to PARylation, other post-translational modifications (e.g. phosphorylation and ubiquitination) stabilize the DDR machinery.