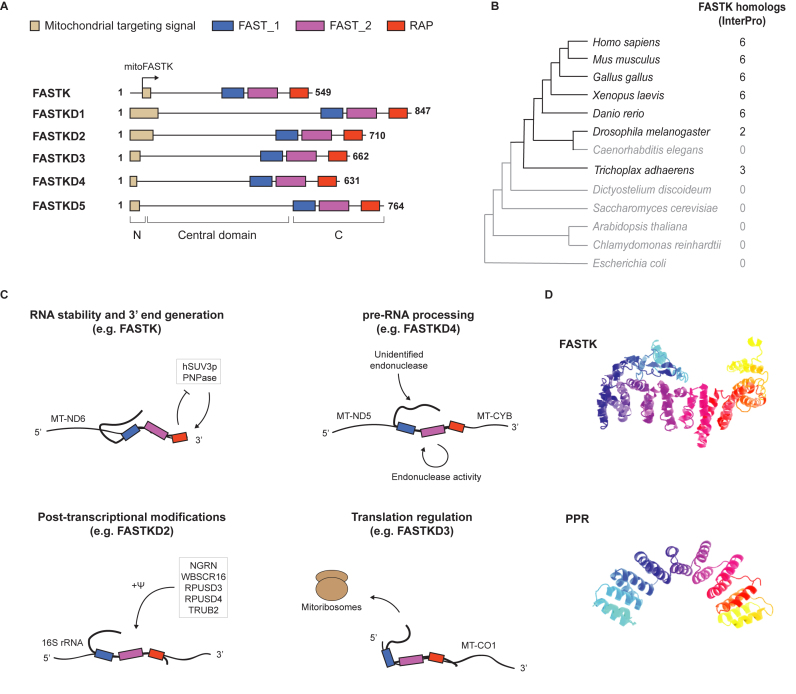
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the FASTK family proteins. N: Amino-terminal domain. C: carboxy-terminal domain. The arrow indicates the internal translation start site in FASTK mRNA that generates mitoFASTK (B) Conservation of the FASTK family across evolution according to InterPro (12). Only proteins containing a FAST_1, FAST_2 and a RAP domain on the same polypeptide are reported. Redundant proteins from the database have been filtered out. (C) Proposed mechanism of action of the members of the FASTK family, as detailed in the main text. Ψ: pseudouridine. (D) (top) I-TASSER prediction of FASTK structure (40) and (bottom) crystal structure of a designed PPR protein (PDB ID: 4WSL) (41).