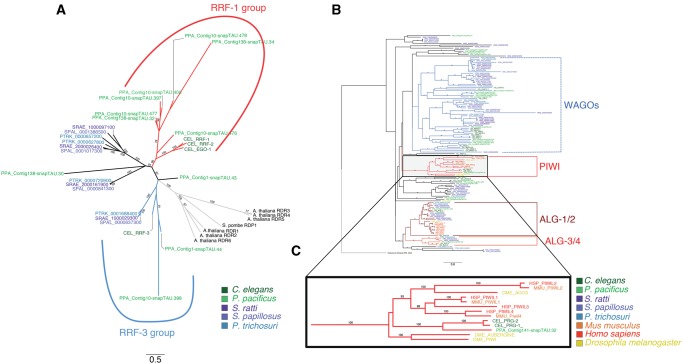
Fig. 4.
—Phylogenetic gene trees for RdRPs and Argonautes. (A) Unrooted neighbour joining tree of the RdRP genes from the five different nematodes. As outgroups we added RdRPs from Arabidopsis thaliana and Saccharomyces pombe. The different species are color-coded, and the two previously described subfamilies (RRF-1 and RRF-3) are indicated by colored branches. Only branch support values ≥ 70 from 100 bootstraps are shown. Notice that the RRF-3 group is not supported by a high bootstrap value. (B) Neighbour joining tree of the Argonaute genes from the five nematodes under study and Drosophila melanogaster, Homo sapiens, Mus musculus and one argonaute gene from the archean species Pyrococcus furiosus. For graphical representation we used FigTree to reroot the tree to the outgroup Argonaute from P. furiosus. The different species are color-coded. The conserved subfamilies that contain nematode, mammalian and Drosophila members are indicated by colored solid branches (ALG-1/2, ALG3/4, PIWI). The previously described group of nematode (worm) specific Argonautes (WAGOs) are indicated by dashed lines. Notice that monophyly of WAGOs is not supported by high bootstrap values in our analysis. For a high resolution graph of the complete tree see supplementary figure 5, Supplementary Material online. (C) Zoom in of the Piwi branch of Argonautes, which is lacking Strongyloididae representatives. Only branch support values ≥70 from 100 bootstraps are shown.