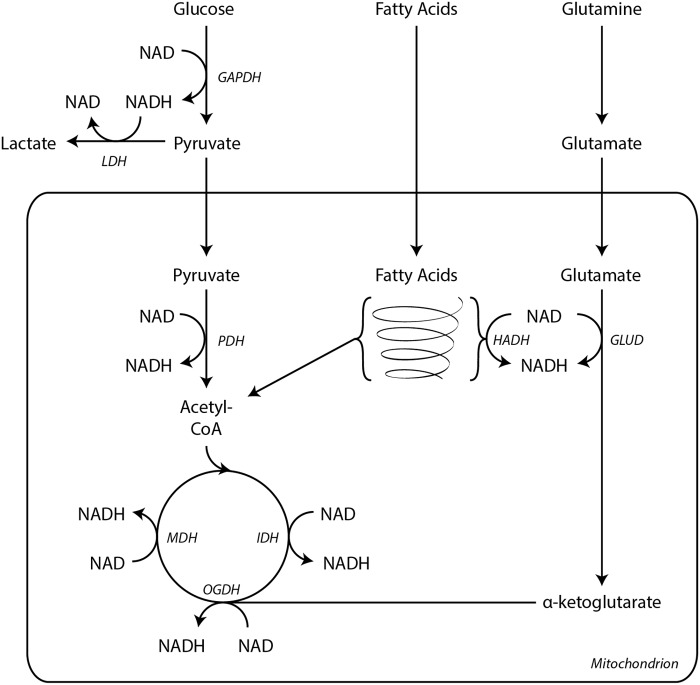
FIG. 6.
NADH wires cells for ATP production. All major catabolic metabolic pathways generate NADH. Glycolysis yields two NADH per glucose molecule through the activity of GAPDH. These NADH are recycled to NAD by LDH. Pyruvate is further oxidized within the mitochondria to acetyl-CoA by PDH, generating an additional molecule of NADH. During fatty acid β oxidation, HADH reduces one NAD molecule per acetyl-CoA liberated. GLUD also generates NADH during glutaminolysis. Three enzymes in the TCA cycle reduce NAD during the oxidation of substrates, IDH, OGDH complex, and MDH. Electrons from NADH then enter the electron transport chain at Complex I. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GLUD, glutamate dehydrogenase; HADH, 3-l-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase; IDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MDH, malate dehydrogenase; OGDH, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid.