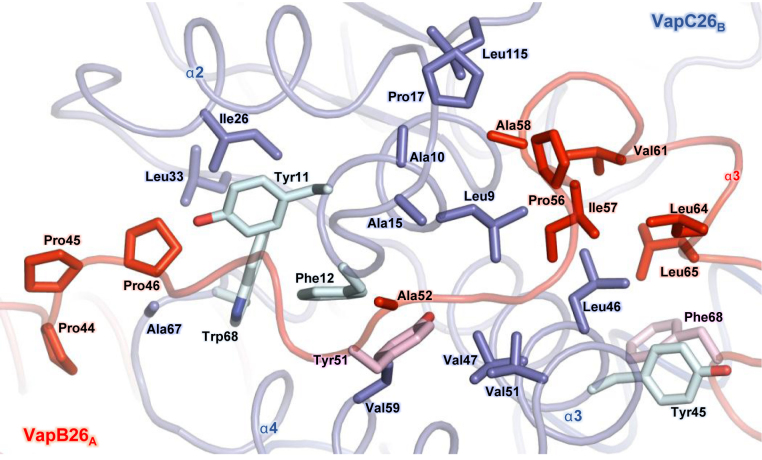
Figure 2.
Heterodimeric interface between VapB26 and VapC26. The residues participating in hydrophobic interactions are shown as stick models. The same colors as those used in Figure 1 are employed. The aromatic residues that exhibit substantial contributions to the hydrophobic interactions in VapB26 and VapC26 are shown in pink and light green, respectively. The driving force required to generate the heterodimer is derived from hydrophobic interactions.