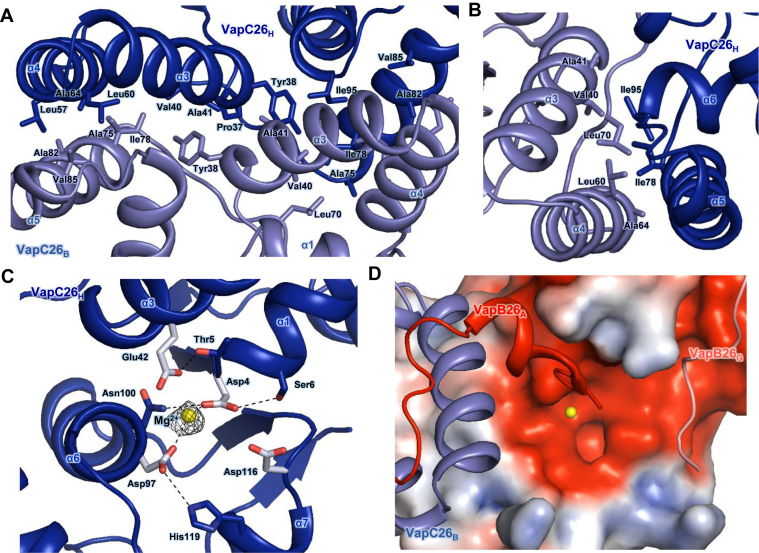
Figure 3.
(A and B) Hydrophobic interface of the VapC26 homodimer. The residues participating in hydrophobic interactions are shown as stick models. (A) Close-up view of the binding interface between two VapC26 monomers. More than 30 residues participate in cross-contacts between the α5 helix of one toxin monomer and the α3 and α4 helices of a neighboring toxin monomer. (B) Range of hydrophobic forces from Ile78 and Ile98. (C and D) Analysis of the active site. Mg2+ is shown in yellow. (C) Fo-Fc composite omit map of Mg2+ site contours at 3σ [calculated with PHENIX (52)]. Hydrogen bonds are shown as black dotted lines. Asp4, Glu42, Asp97, Asp116 and Mg2+ organize the active site. (D) The electrostatic surface potential of VapC26.