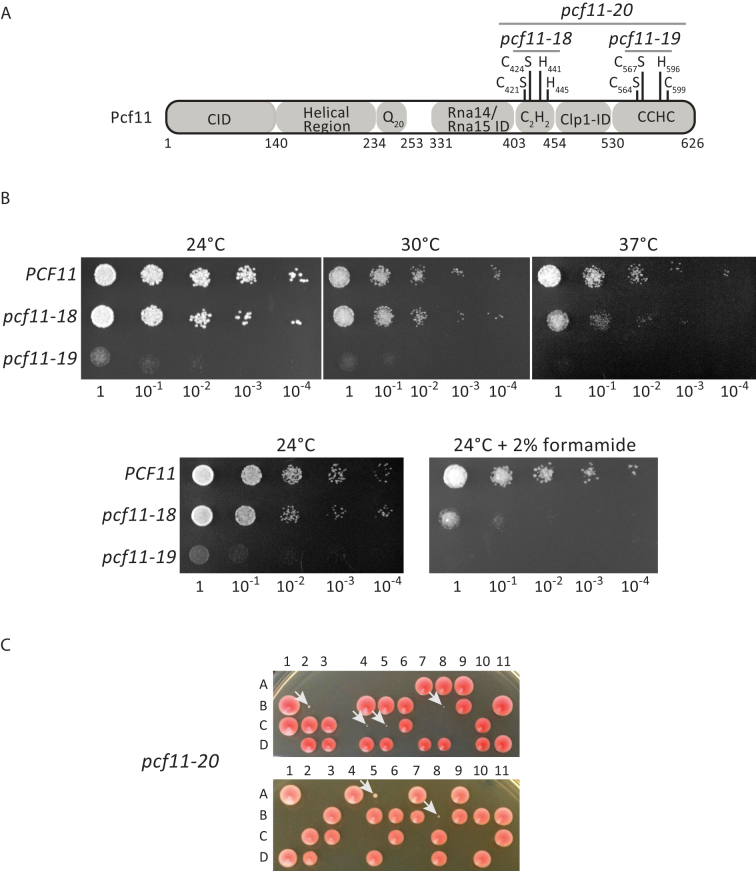
Figure 1.
Effect of mutations of the Pcf11 zinc-binding residues on yeast viability. (A) Schematic diagram of Pcf11 domain organization. The zinc-binding residues are labelled as the point mutations and the relevant alleles. CID: RNAP II large subunit Carboxy-terminal domain Interacting Domain; ID: Interaction Domain. (B) Phenotypic analysis of the wild-type PCF11 and mutant pcf11-18 (C421S/C424S) and pcf11-19 (C564S/C567S) strains. Ten-fold serial dilutions were plated on rich medium (YPDA) and analysed at 24, 30 and 37°C, and at 24°C on YPDA containing 2% formamide. (C) Tetrad analysis after meiosis of two independent diploid strains of YLM232 (pcf11Δ::HIS3/PCF11) transformed with the plasmid-borne pcf11-20 allele (C421S/C424S/C564S/C567S). The four spores (A, B, C, D) coming from the same ascus (numbered horizontally) are arranged vertically. The slow growing spores corresponding to the pcf11-20 mutants are indicated with a white arrow (spores 2B, 4C, 5C, 8B from the first diploid, and spores 5A, 8B from the second diploid).