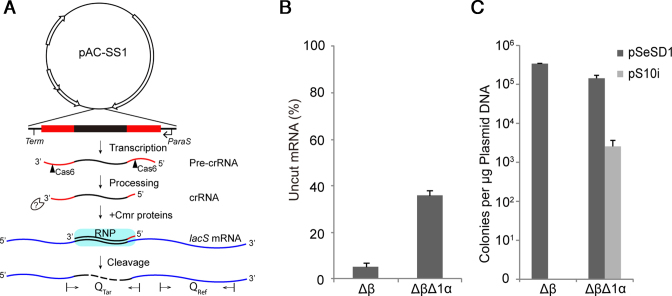
Figure 1.
Effect of cmr1α deletion on RNA and DNA interference by Cmr-α in S. islandicus. (A) Schematic of in vivo RNA interference activity assay in S. islandicus using artificial CRISPR plasmids (pAC). pAC-SS1, an artificial mini-CRISPR plasmid producing a crRNA that guides Cmr-α proteins to target the SS1 protospacer of lacS mRNAs for degradation. Two primer sets, Qtar and Qref designed for amplification of PCR products from the target region and a reference region, respectively, are indicated on the lacS mRNA. (B) Quantification of mRNAs expressed from the chromosomal lacS gene in different S. islandicus strains by qRT-PCR. Total RNAs were extracted from transformants of pAC-SS1 and pSe-RP, the latter of which a Sulfolobus artificial mini-CRISPR cloning vector (reference plasmid), and lacS mRNA levels were estimated by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent standard deviations of replicates determined for three independent transformants for each plasmid. Amounts of uncut mRNA are determined as the ratio of the amounts of SS1 RNA protospacer in pAC-SS1 transformants versus those determined for the corresponding pSe-RP transformants. (C) In vivo DNA interference activity assayed in different S. islandicus strains by an invader plasmid assay. pSeSD1—a shuttle vector for Sulfolobus, pS10i—an invader plasmid carrying a target sequence of spacer 10 in CRISPR locus 2 in S. islandicus REY15A. Δβ—S. islandicus Δβ: a reference strain that carries a deletion of the complete Cmr-β gene cassette; ΔβΔ1α—S. islandicus ΔβΔ1α: derived from S. islandicus Δβ from which the cmr1α gene was deleted. All strains were derived from the genetic host S. islandicus E233 that carries the β-glycosidase (lacS) gene.