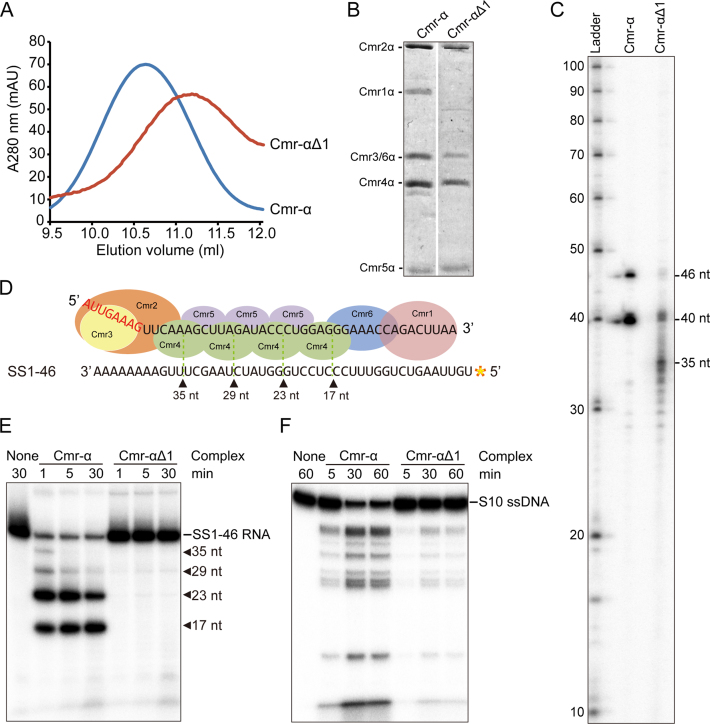
Figure 2.
The core Cmr-α complex lacking Cmr1 is active in nucleic acid interference. (A) Gel filtration profiles of Cmr-α (blue) and Cmr-αΔ1 (red). The latter is composed of Cmr2–6α. A280: UV absorbance at 280 nm. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified Cmr-α and Cmr-αΔ1 complexes. (C) crRNAs present in Cmr-α and Cmr-αΔ1 complexes. RNAs were extracted from Cmr-α and Cmr-αΔ1, 5′-labeled with radio-active γ-32P-ATP and analyzed by denaturing PAGE. Ladder: RNA size ladder (nt). (D) Schematic of cleavage sites on SS1–46 RNA by Cmr-α complex. (E) RNA cleavage assay. 50 nM Cmr-α and Cmr-αΔ1 complexes were incubated with 25 nM labeled SS1–46 RNA for indicated time points. Then, the samples were analyzed by denaturing PAGE. (F) RNA-activated DNA cleavage assay. Each reaction contained 25 nM of labeled ssDNA, 200 nM SS1–46 RNA and 50 nM effector complex. After incubation at 70°C for 1 h, cleavage products were analyzed by denaturing PAGE.