Figure 3. Immobilized human rCD63 is able to bind fibrillar Aβ in an in vitro binding assay.
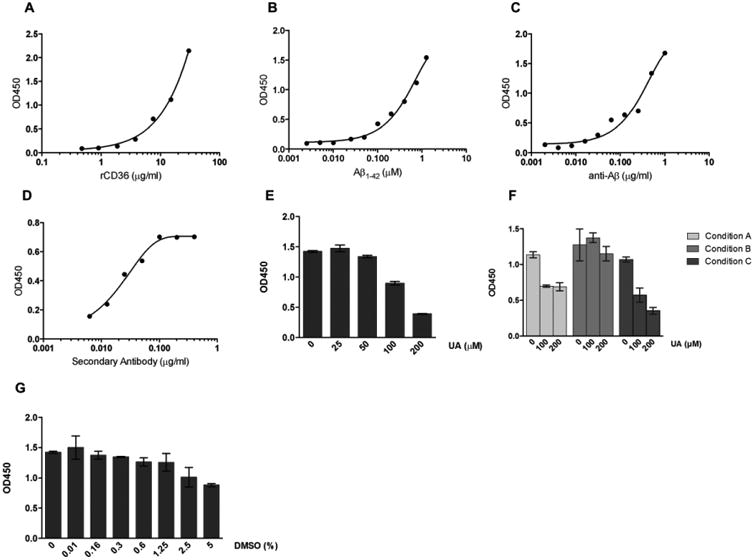
Assay parameters were optimized to achieve best possible signal to noise ratio. (A-D) Curves from checkerboard titrations to determine optimal concentrations for rCD36 (A), fibrillar Aβ (B), anti-Aβ primary antibody (C) and secondary anti-species conjugated antibody (D). (E) Dose response graph of the Ursolic acid (UA) positive control. (F) Optimization of time of addition of inhibitors in the assay. Condition A: the addition of UA and fAβ 1-42 at the same time; Condition B: UA added 30 minutes before and removed just before adding the fAβ 1-42 and; Condition C: UA added 30 minutes before fAβ 1-42 addition. (G) Sensitivity of the assay to DMSO. Results represent means ± S.D. from samples assayed in duplicate.
