Figure 5. Compounds inhibiting CD36-Aβ interaction also impair the pro inflammatory activation of macrophages.
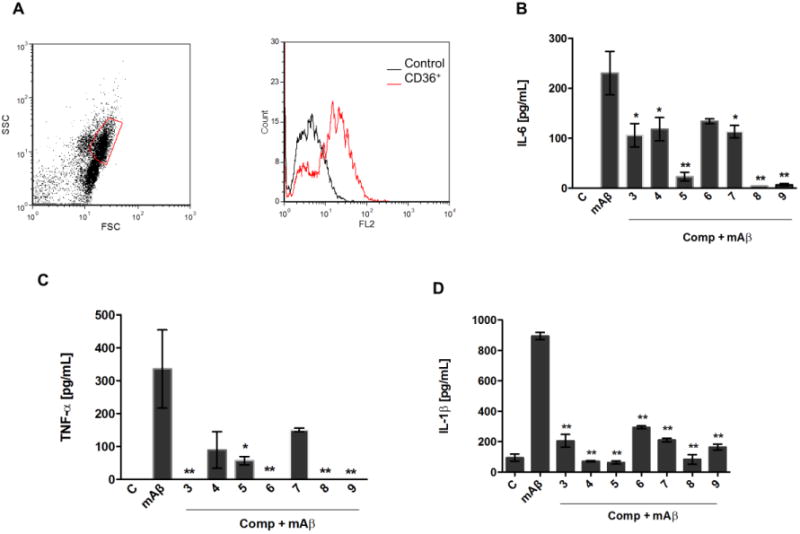
Peritoneal macrophages from C57Bl/6 mice were collected for FACS analysis of CD36 expression. Representative dot plot and histogram of CD36 expressing cells are shown from two different experiments (A). Macrophages were stimulated with fibrils of mouse Aβ1-42 (30 μM) in the presence or absence of compounds (30 μM). Supernatants were harvested 16 h later and concentrations of IL- 6 (B) and TNF-α (C) were measured by the ELISA method. (D) LPS-primed macrophages were stimulated for 6 hours with fibrils of mouse Aβ 1-42 (30 μM) with or without compounds. IL-1β concentration was detected by ELISA. Results represent means ± S.E.M. from stimuli performed in duplicates and are representative of two different experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, compared with mAβ1-42 stimulus alone.
