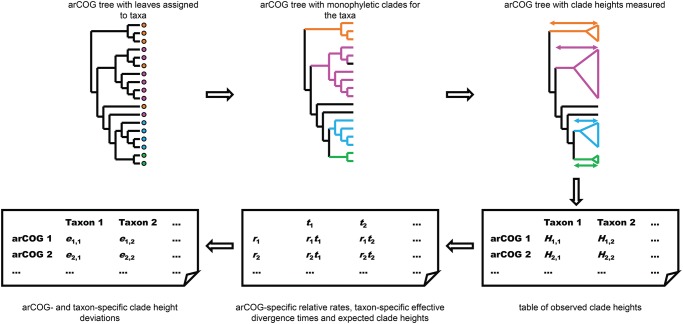
Fig. 1.
—Computational pipeline for identification of evolutionary rate deviations from phylogenetic trees. The main steps of the computational pipeline developed and applied here for the detection of evolutionary rate deviations in phylogenetic trees of arCOGs are shown. (A) Detection of monophyletic groups (clades) in arCOG trees. The deepest clades satisfying the purity and coverage criteria are identified for all well-represented taxa in all arCOG trees. Empty circles indicate the tree clades that are analyzed; filled circles indicate the clades that were identified for the given taxa in the given tree. (B) Calculation of the distance deviation for selected clades. The table of observed clade heights is decomposed into the expected distances rC tT and deviations eT, C; distance deviations (in the log scale) for all clades are recorded.