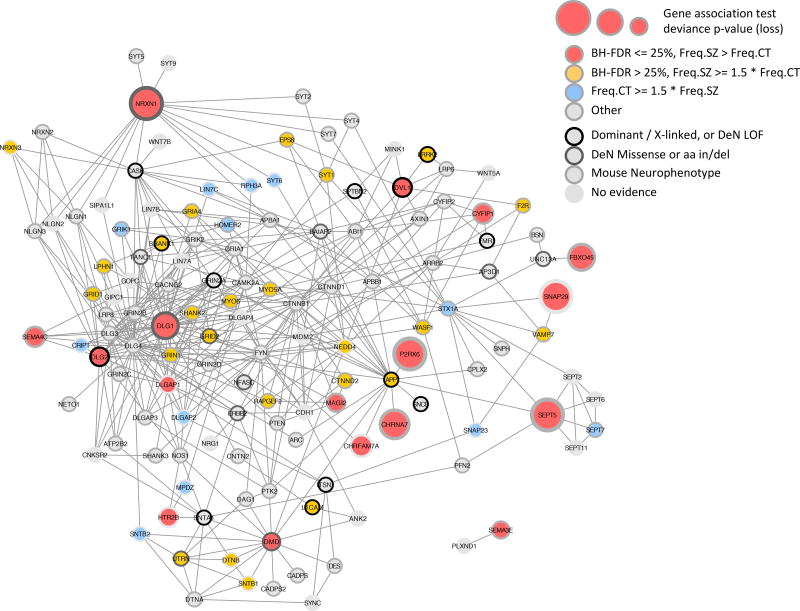
Figure 3. Protein Interaction Network for Synaptic Genes.
Synaptic and ARC-complex genes intersected by a rare loss in at least 4 case or control subjects and with genic burden Benjamini-Hochberg FDR <= 25% (red discs) were used to query GeneMANIA36 and retrieve additional protein interaction neighbors, resulting in a network of 136 synaptic genes. Genes are depicted as disks; disk centers are colored based on rare loss frequency (Freq.SZ and Freq.CT) being prevalent in cases or controls; disk borders are colored to mark (i) gene implication in human dominant or X-linked neurological or neurodevelopmental phenotype, (ii) de novo mutation (DeN) reported by Fromer et al. 28, split between LOF (frameshift, stop-gain, core splice site) and missense or amino acid insertion / deletion, (iii) implication in mouse neurobehavioral abnormality. Pre-synaptic adhesion molecules (NRXN1, NRXN3), post-synaptic scaffolds (DLG1, DLG2, DLGAP1, SHANK1, SHANK2) and glutamatergic ionotropic receptors (GRID1, GRID2, GRIN1, GRIA4) constitute a highly connected subnetwork with more losses in cases than controls.