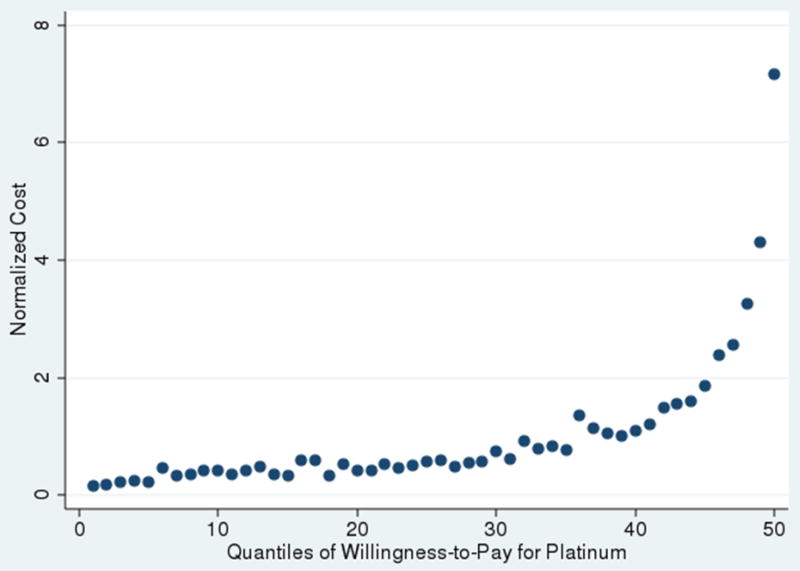
Figure A2. Correlation between Willingness-to-Pay for Platinum and Total Costs.
Notes: In the figure, 50 quantiles of willingness-to-pay are on the x-axis and normalized total medical spending (spending divided by average spending) is on the y-axis. Willingness-to-pay is generated using the expected utility model presented in the text along with the parameters of the model estimated using the choice model. A positive correlation between willingness-to-pay and total costs implies that as the price differential between Platinum and Bronze decreases, the marginal Platinum enrollee will have a lower cost than the average Platinum enrollee, i.e. the Platinum plan will be adversely selected.