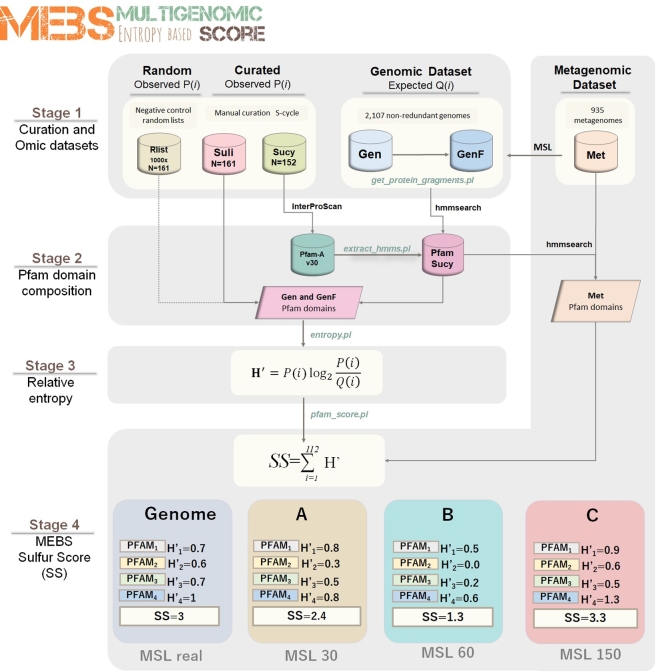
Figure 1:
Schematic representation of the 4 stages of the MEBS algorithm focusing on the S-cycle. The first step consists of the systematic curation of a database containing the metabolic information of the S-cycle, which is reduced to a FASTA file of proteins involved (Sucy) and a list of 161 related microorganisms (Suli). A thousand lists of 161 random-sampled genomes were used as negative control (Rlist). The training dataset comprises 2107 genomes (Gen), which were fragmented in different sizes by considering the mean size length (MSL) of 935 metagenomes (Met). In the second stage, the domain composition of Sucy proteins is obtained by scanning Pfam-A, resulting in the Pfam-Sucy database. Then, the relative entropy (H΄) of each Sucy-Pfam domain is obtained in the third stage. Finally, the precomputed entropies in Gen and GenF are used to evaluate full-length genomic sequences (real) and metagenomic sequences of variable MSL (in this example A, B, and C).