Figure 4.
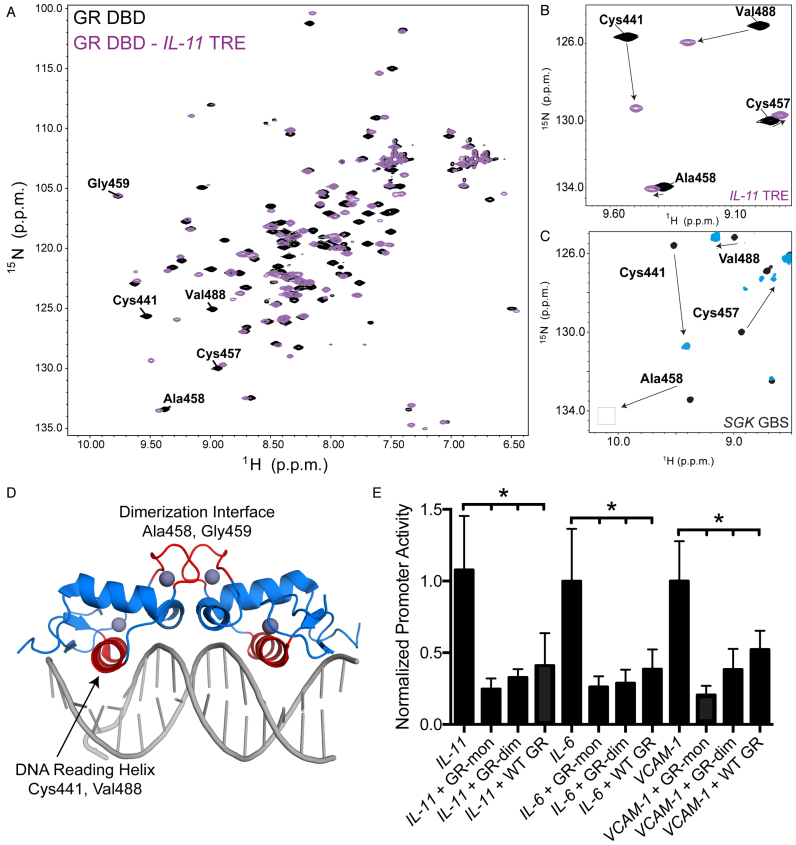
Monomeric GR is preferred to repress inflammatory genes. (A) 2D [1H,15N]-HSQC NMR analysis of 15N-GR DBD binding to IL11 TRE DNA; data for GR DBD alone is shown in black and the GR DBD:IL11 complex shown in purple. (B) Zoom-in view of the 2D NMR data show that residues contacting DNA in the complex, including Cys441 and Val488, show significant chemical shift perturbations upon binding DNA. Residues in the dimerization loop (D loop) do not show perturbations, suggesting GR binds as a monomer to IL11 TRE. (C) D loop residues show perturbations when GR binds as a dimer on a canonical GBS. (D) GR DBD-GBS crystal structure (PDB: 3FYL) with the DNA reading helix and D loop highlighted in red. Residues highlighted in panels a-c are located within these two regions. (E) Dimerization deficient mutants GRdim (Ala458Thr) and GRmon (Ala458Thr/Ile634Ala) cause more repression of the constitutively active TRE luciferase reporters compared to WT GR.