Fig. 2.
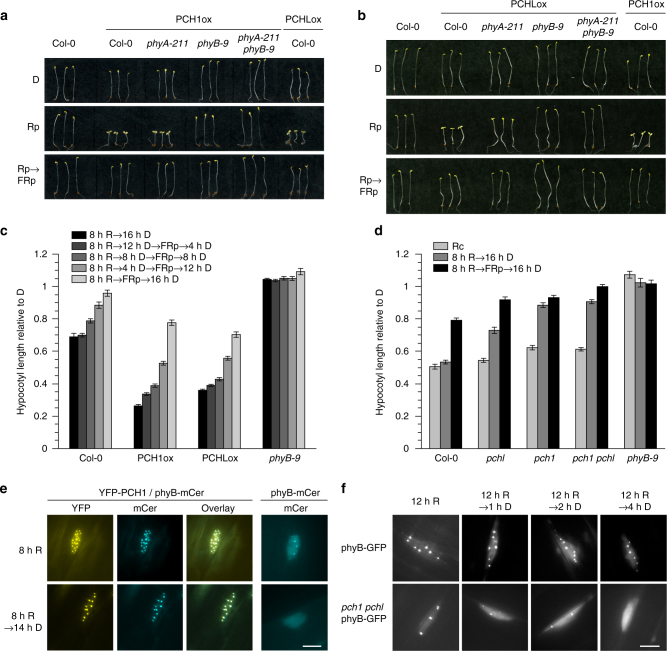
PCH1 and PCHL stabilise phyB in the active state in planta. a, b PCH1ox and PCHLox seedlings respond to red light pulse treatments (Rp). Wild type (Col-0) and mutant seedlings expressing either HA-YFP-PCH1 (PCH1ox) (a) or HA-YFP-PCHL (PCHLox) (b) were grown for 4 days in darkness on filter paper soaked with water. The seedlings were either treated with a single red light pulse (Rp, 5 min, 50 μmol m−2 s−1) per day, or a Rp followed by a long-wavelength FR pulse (FRp, 776 nm, 5 min, 50 μmol m−2 s−1) (Rp → FRp). Control seedlings were kept in darkness (D). See Supplementary Fig. 4 for quantification of hypocotyl lengths and experiments with seedlings grown on 0.5× MS medium. c High levels of active phyB are maintained during the dark phase in PCH1ox and PCHLox seedlings. Wild type (Col-0), PCH1ox, PCHLox, and phyB-9 seedlings were grown for 4 days in 8 h red (R, 50 μmol m−2 s−1)/16 h dark (D) cycles and given a long-wavelength far-red light pulse (FRp, 776 nm, 5 min, 50 μmol m−2 s−1) at time points after lights-off. Control seedlings were kept in darkness (D). d The end-of-day far-red (EOD-FR) response requires PCH1 and PCHL. Wild type (Col-0) and mutant seedlings were grown as in c, except either constant red light (Rc), an immediate far-red light pulse (8 h R → FRp → 16 h D), or no far-red light pulse (8 h R → 16 h D) were used. c, d Mean hypocotyl length relative to dark-grown seedlings is shown. Error bars indicate ± s.e.m.; n ≥ 20. e, f Subnuclear localisation of PCH1 and phyB was analysed by fluorescence microscopy. Scale bar = 5 µm. e PCH1 stabilises phyB photobodies. Four-day-old etiolated seedlings expressing phyB-mCer in phyB-9 or HA-YFP-PCH1 (PCH1ox) backgrounds were exposed to red light (R, 10 μmol m−2 s−1) for 8 h, followed either by 0 or 14 h incubation in darkness (D). Data for phyB-mCer single transgenic seedlings are duplicated in Supplementary Fig. 7a. f PhyB photobodies are highly unstable in the pch1 pchl mutant. Four-day-old etiolated seedlings expressing phyB-GFP in wild type or pch1 pchl backgrounds were exposed to red light (R, 50 μmol m−2 s−1) for 12 h followed by incubation in darkness (D)