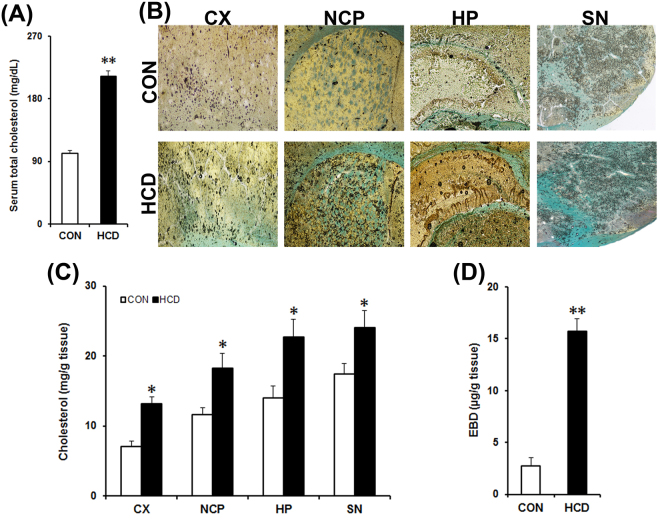
Figure 3.
High-cholesterol diet causes hypercholesterolemia, increases cholesterol level in brain and disrupts blood-brain barrier (BBB). Control (CON) mice received normal diet and the HCD group received high-cholesterol diet (at 5% w/w mixed with normal diet) for 12 weeks and sacrificed on the last day. (A) Cholesterol level in blood serum (n = 8). (B) Cholesterol level in brain. Brain cholesterol level was assayed histologically in paraformaldehyde fixed tissue sections following Schultz’s method. Photographs are representative sections showing the cortex (CX), striatum (NCP), hippocampus (HP) and substantia nigra (SN) from control and HCD mice. The blue or greenish-blue colour denotes cholesterol. The dark circles denote air bubbles formed as a result of acid (sulphuric acid: acetic acid) reaction. Photographs were taken at 4× magnification. (C) Estimation of brain cholesterol level. Cholesterol level was estimated from tissue homogenates of CX, NCP, HP and SN regions of brain by using kit (n = 6). (D) BBB disruption. Evans Blue dye (EBD) extraversion in brain tissues were analysed for possible disruption of BBB using a Spectrophotometric method (n = 4). The results are mean ± S.E.M. *P ≤ 0.05 or **P ≤ 0.01 as compared to control. Data of cholesterol level in serum (A) and brain EBD were analyzed using an unpaired Student’s t-test (D), and brain cholesterol levels were analyzed using a two-way repeated measure ANOVA (C).