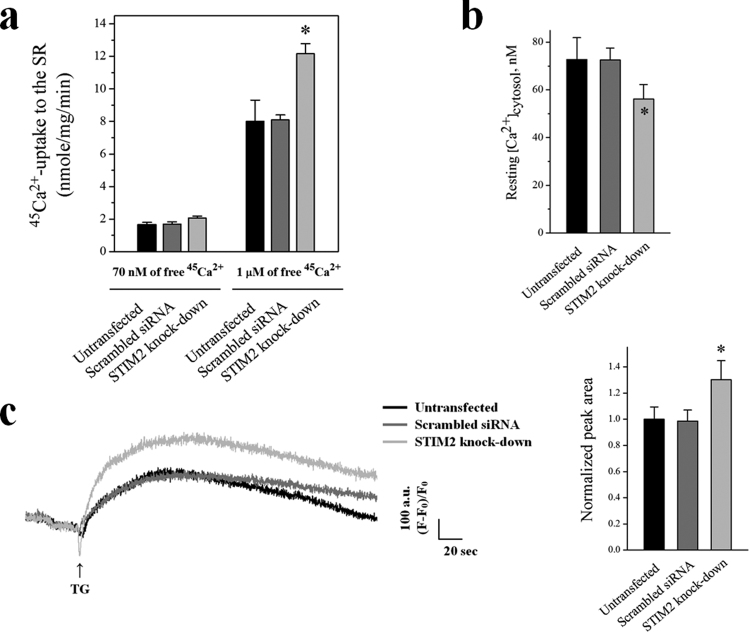
Figure 3.
Increases in 45Ca2+-uptake into the SR through SERCA1a and the amount of Ca2+ in the SR, and a decrease in the cytosolic Ca2+ level at rest by STIM2-knockdown. (a) Oxalate-supported 45Ca2+-uptake into the SR through SERCA1a using the homogenate of the STIM2-knockdown myotubes was measured at 70 nM or 1 μM of free 45Ca2+. Either an untransfected or a scrambled siRNA-transfected control was used as a negative control. The results are presented as the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments (Table 3). *Significant difference compared with the untransfected control (p < 0.05). The STIM2-knockdown myotubes showed a significantly increased 45Ca2+-uptake through SERCA1a only at 1 μM of free 45Ca2+. (b) Cytosolic Ca2+ level at rest was examined in the STIM2-knockdown myotubes, and histograms are shown for the mean values of each. *Significant difference compared with the untransfected control (p < 0.05). The values are presented as the mean ± S.E. for the number of myotubes shown in the parentheses of Table 4. Cytosolic Ca2+ level at rest was decreased by STIM2-knockdown. (c) To measure the amount of Ca2+ in the SR, TG was applied to the STIM2-knockdown myotubes in the absence of extracellular Ca2+ to avoid extracellular Ca2+ entry. A representative trace for each group is shown, and the results are summarized as bar graphs in the right-hand panel. *Significant difference compared with the untransfected control (p < 0.05). The values are presented as the mean ± S.E. for the number of myotubes shown in the parentheses of Table 4. The amount of Ca2+ in the SR was significantly increased by STIM2-knockdown.