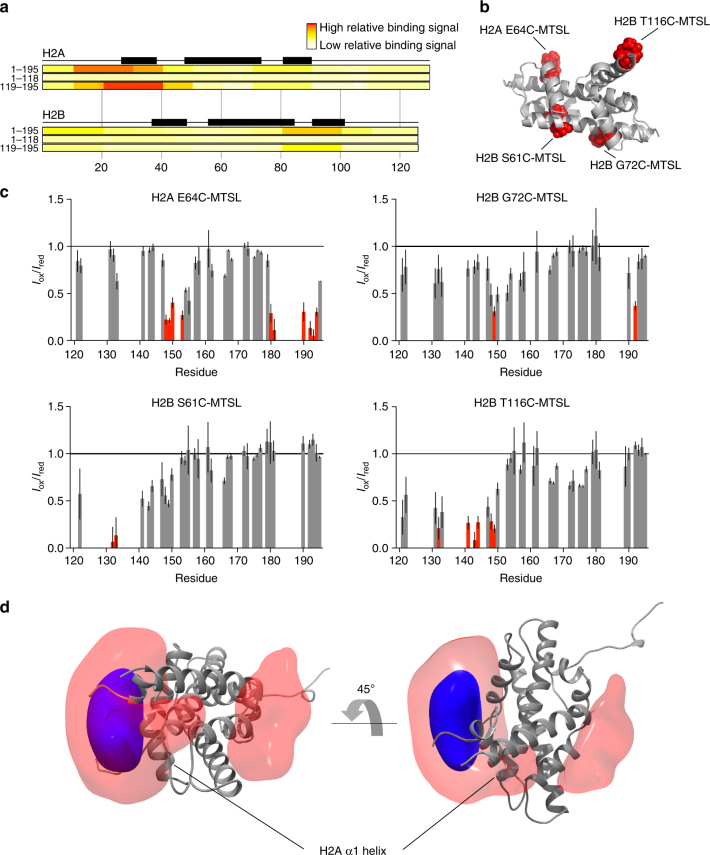
Fig. 5.
Mechanisms of H2A/H2B binding by the Npm tail domain. a Histone peptide array result using three different Npm truncations probed against comprehensive H2A/H2B peptides on a chip. Top = full-length Npm (1–195), middle = Npm core (1–118), bottom = GST-tagged Npm tail (119–195). Black boxes represent positions of α-helices in the histone fold. b Positions of MTSL paramagnetic spin labels on the H2A/H2B dimer structure. Histone tails removed for clarity. c I ox/I red graphs of the Npm tail domain bound to H2A/H2B at 400 µM concentration. Four sets of intermolecular PRE effects derived from the complex. Error bars are inversely proportional to the propagated signal-to-noise ratio of individual resonances. Same coloring scheme as used in Fig. 3a. d Reweighted atomic probability density maps indicating the most likely positions of A2 around the H2A/H2B dimer (gray ribbon, histone tails removed for clarity). Transparent red contoured at 10%, and solid blue contoured at 50%. Two distinct binding sites are consistent with the PRE data