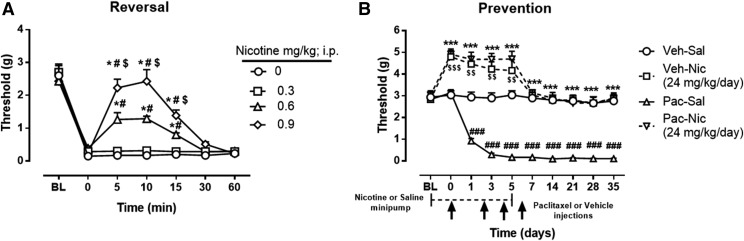
Fig. 1.
Antinociceptive and preventative effect of nicotine in a mouse model of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. (A) Reversal of mechanical allodynia by acute administration of nicotine at doses of 0.3, 0.6, and 0.9 mg/kg i.p. in paclitaxel-treated mice at days 7–14 after initial paclitaxel injection. *P < 0.0001 versus saline (0 mg/kg); #P < 0.0001 versus nicotine (0.3 mg/kg); $P < 0.0001 versus nicotine (0.6 mg/kg). (B) Prevention of mechanical allodynia by chronic administration of nicotine at a dose of 24 mg/kg per day. Arrows indicate vehicle/paclitaxel injections on days 0, 2, 4, and 6. Minipumps with nicotine were implanted s.c. in the mouse, starting 2 days before the vehicle/paclitaxel treatment cycle and ending on day 5. Baseline measurements were taken at baseline before saline/nicotine minipump implantation and on day 0 before paclitaxel/vehicle administration. ***P < 0.001 Pac-Nic versus Pac-Sal; ###P < 0.001 Pac-Sal versus Veh-Sal; $$$P < 0.001, $$P < 0.01 Veh-Nic versus Veh-Sal. BL, baseline; Nic, nicotine; Pac, paclitaxel; Sal, saline; Veh, vehicle. n = 8 per group; data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. Statistical analysis: for mice treated with 24 mg/kg nicotine, a 2 × 2 × 10 mixed-factor ANOVA of chemotherapy drug (paclitaxel or vehicle) in nicotine- or saline-treated mice by day showed a significant three-way interaction [F(9,252) = 7.851, P < 0.001]. A subsequent 2 × 10 mixed-factor ANOVA of paclitaxel or vehicle treatment by day was calculated for each level of treatment (nicotine or saline). Saline-treated mice demonstrated a significant interaction of chemotherapy drug (paclitaxel or vehicle) by day [F(9,252) = 15.054, P < 0.001], where a Sidak post hoc test revealed a lower threshold responding in paclitaxel-treated mice compared with vehicle-treated mice on days 0–35 (P < 0.001). A separate 2 × 10 mixed-factor ANOVA calculated where nicotine or saline treatment by day differed at each level of chemotherapy drug (paclitaxel or vehicle). Paclitaxel-treated mice demonstrated a significant interaction of drug pretreatment (nicotine or saline) by day [F(9,252) = 6.703, P < 0.001], where a Sidak post hoc test revealed a higher threshold responding in nicotine-treated mice compared with saline-treated mice on days 0–35 (P < 0.001). Vehicle-treated mice also demonstrated a significant interaction of drug pretreatment (nicotine or saline) by day [F(9,252) = 37.064, P < 0.001], where a Sidak post hoc test revealed a higher threshold responding in nicotine-treated mice compared with saline-treated mice, but only on days 0, 1, and 3 (P < 0.001).