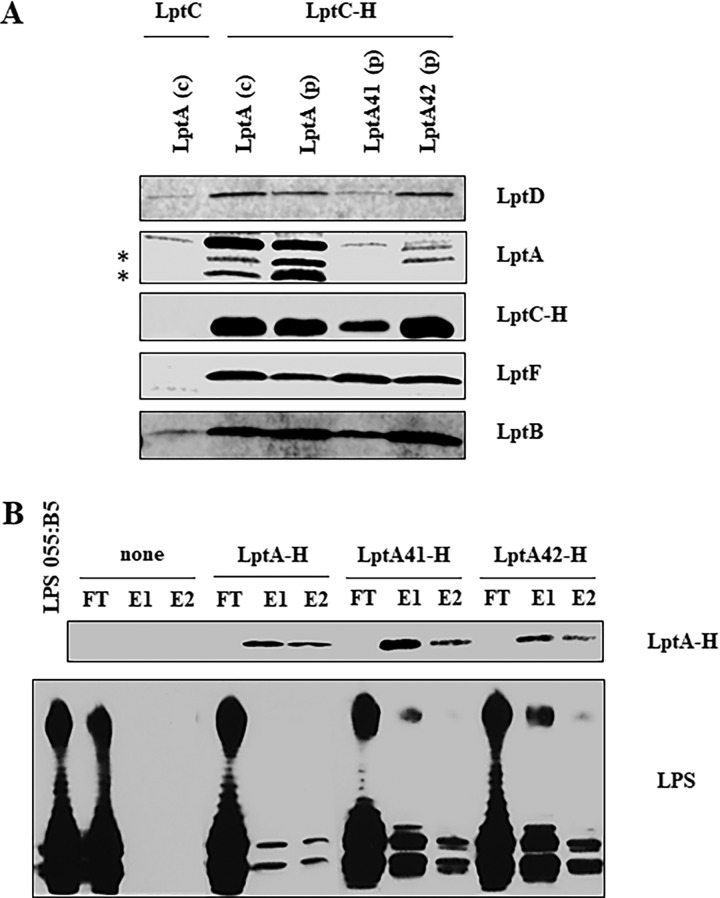
FIG 4.
Lpt complex assembly and LPS binding by LptA mutants. (A) Assembly of wild-type and mutant LptA proteins into the Lpt complex. Total membranes were collected from strains AM604 expressing chromosomal LptA [LptA (c)], PS001 ectopically expressing LptA [LptA (p)], PS003 ectopically expressing LptA41 [LptA41 (p)], PS111 ectopically expressing LptA42 [LptA42 (p)] harboring pGS108 expressing His-tagged LptC (LptC-H), or pGS103 expressing the nontagged LptC (LptC) as a negative control. Samples were solubilized with DDM and affinity purified using a Talon metal affinity resin. The proteins were then fractionated by SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotting was performed with anti-LptD, anti-LptF, anti-LptB, and anti-His (to detect LptC-H) antibodies. For LptA detection, samples were analyzed by Tricine SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotting was performed using anti-LptA antibody. The asterisks indicate degradation products of LptA. (B) Binding of wild-type and mutant LptA proteins to LPS. The abilities of His-tagged LptA, LptA41, and LptA42 to bind purified LPS were assessed by their coelution from Ni-NTA chromatography resin. LPS and the purified His-tagged proteins were incubated and affinity purified on Ni-NTA resin as described in Materials and Methods. As a negative control, LPS was incubated without any added protein (none). FT, flowthrough; E1 and E2, elutions. To monitor LPS-LptA complex formation, equal volumes of the collected chromatographic fractions were analyzed by denaturing gel electrophoresis. LptA-H protein was detected by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with anti-His antibodies; for LPS visualization, samples were analyzed by Tricine SDS-PAGE, and Western blotting was performed with anti-lipid A core antibodies.