FIG 2.
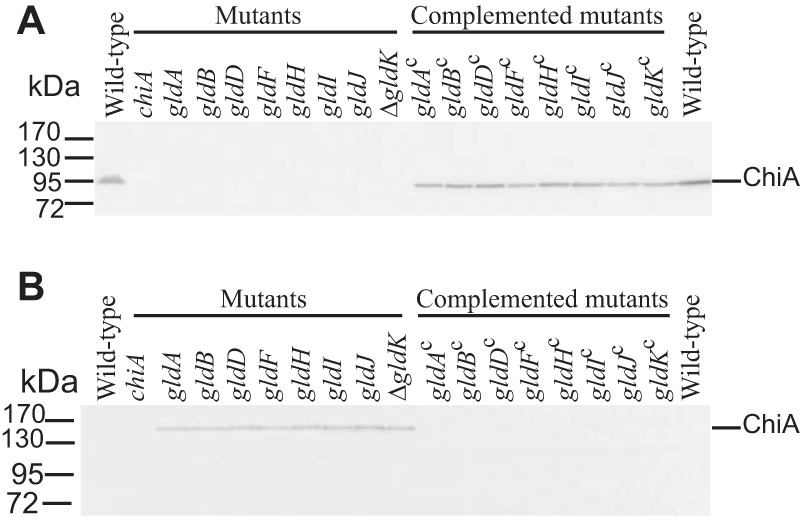
Mutations in gldA, gldB, gldD, gldF, gldH, gldI, and gldJ result in defects in secretion of the soluble extracellular chitinase ChiA. Cell-free spent medium (A) and cells (B) were examined for ChiA by SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blot analysis using antiserum against recombinant ChiA. ChiA is proteolytically processed during or after secretion, as previously reported (16), accounting for the smaller size in panel A. The cells analyzed were wild-type F. johnsoniae UW101, chiA mutant CJ1808, gldA mutant UW101-288, gldB mutant CJ569, gldD mutant CJ282, gldF mutant CJ787, gldH mutant CJ1043, gldI mutant UW102-41, gldJ mutant UW102-80, and ΔgldK mutant CJ2122. gldAc, gldBc, gldDc, gldFc, gldHc, gldIc, gldJc, and ΔgldKc are complemented versions of the mutants that carry pSA21, pDH223, pMM209, pMK314, pMM293, pMM291, pMM313, and pTB99, respectively. Samples loaded in panel B corresponded to 15 μg of protein per lane, and samples loaded in panel A corresponded to the volume of spent medium that contained 15 μg of cell protein before the cells were removed.
