Fig. 6.
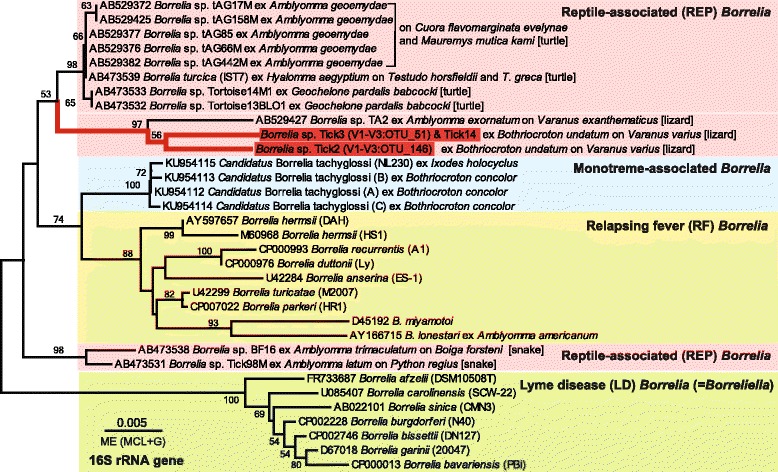
The evolutionary history of the reptile associated Borrelia 16S rRNA gene sequences. The tree was inferred using the Minimum Evolution (ME) method, with evolutionary distances computed using the Tajima-Nei method (TN), and the rate variation among sites modelled with a gamma distribution (+G, shape parameter = 0.28) in MEGA7. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (500 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The analysis involved 33 nucleotide sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 1075 positions in the final dataset. Accession numbers and species name and strain are depicted on the right. Colour coded major clades within Borrelia species include the monophyletic Lyme disease Borrelia (=Borreliella), the monophyletic Relapsing fever Borrelia, the monotreme-associated Borrelia, and the polyphyletic reptile-associated Borrelia, including turtle, lizard and snake groups
