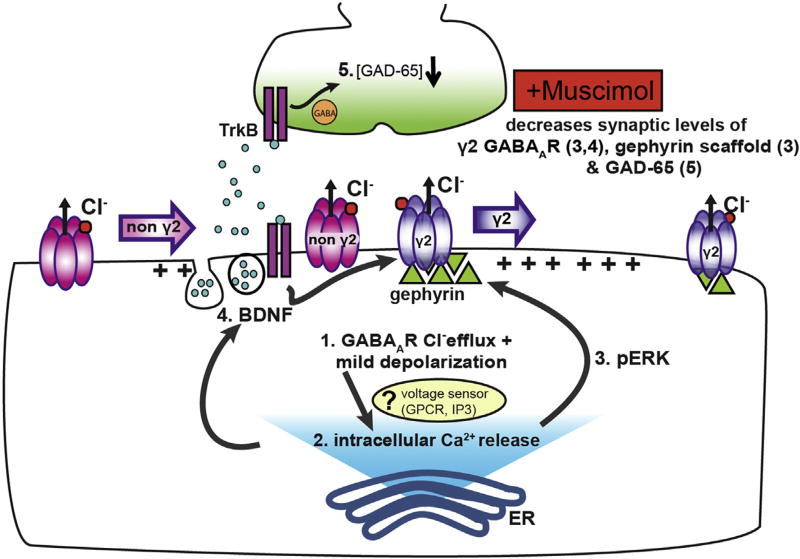
Fig. 10.
Model for muscimol induced GABAergic synaptic plasticity. Synaptic GABA release in neurons with established synapses produces mild depolarization via chloride efflux and low release of intracellular Ca2+ from ER stores, resulting in low pERK levels and minimal BDNF stimulation. Prolonged exposure to muscimol enhances depolarization (1) and increases Ca2+ store release (2), potentially via a Ca2+ influx independent voltage sensor. Ca2+ store release in turn activates ERK above baseline (3) and promotes release of dendritic BDNF (4). Enhanced pERK activity decreases synaptic γ2 GABAAR and gephyrin, leading to higher extrasynaptic γ2 GABAAR levels (3). BDNF signaling contributes to the decrease in synaptic γ2 GABAAR (4), as well as diminishing presynaptic GAD65 levels (5).