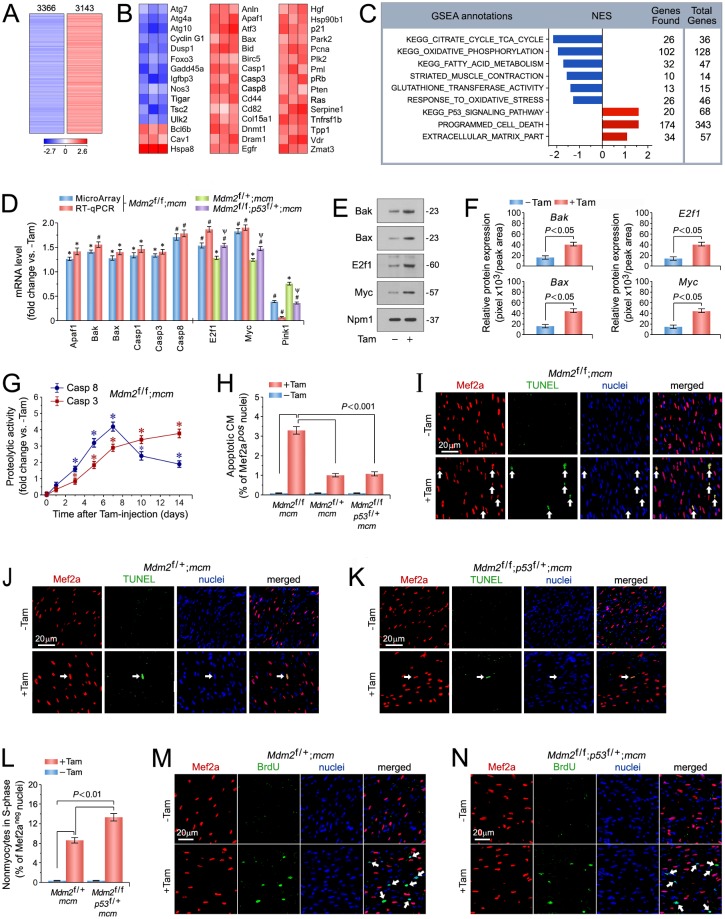
Fig 4. p53 is spontaneously active in Mdm2-deficient cardiomyocytes and induces apoptosis.
(A) Genome-wide messenger RNA (mRNA) microarray profiling reveals that conditional genetic ablation of Mdm2 induces profound alterations in the cardiac transcriptome indicating a high degree of complexity associated with Mdm2-deficiency. Heat map of unsupervised hierarchical cluster analysis at a high confidence threshold identifies 6,509 transcripts (rows) out of 26,166 individual genes (columns) that were enriched in the hearts of Mdm2f/f;mcm mice post-Tam relative to vehicle-injected controls. Values (log2 expression) are shown by color and intensity of shading. Blue, repressed. Red, induced. n = 3 biological replicates. P < 0.01. Fold change >1.3. Mice (13 weeks old) were analyzed at 14 days post-Tam. (B) Heat maps examining the impact of genomic modifications in Mdm2-deficient hearts (columns) on previously validated p53 target genes (rows). Values, log2 expression. n = 3. P < 0.01. Fold change >1.3. (C) Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) of biological processes among all differentially expressed transcripts, assessed by overrepresentation of GSEA terms for the biological function of each transcript in hearts of Mdm2f/f;mcm mice post-Tam. NES, normalized enrichment score. NES have False Discovery Rate (FDR) q-values <0.1. Blue, inhibited processes. Red, activated processes. (D) Expression levels of key genes selected from top-ranked gene sets identified in Fig 4A, involved in the regulation of cardiomyocyte apoptosis in the indicated Mdm2 and p53 mutant mice as analyzed by RT-qPCR at 7 days post-Tam. n = 3. *P < 0.05 vs. -Tam. #P < 0.01 vs. -Tam. Ψ < 0.05 vs. Mdm2f/+;mcm and Mdm2f/f;mcm. (E) Immunoblot analysis of master regulators of apoptosis in Mdm2f/f;mcm mice at 7 days post-Tam employing specific antibodies as indicated on the left. One representative immunoblot of 3 independent experiments is shown. (F) Protein levels shown in Fig 4E were quantified with ImageJ software. n = 3. (G) Time course of caspase 3/8 activation in Mdm2f/f;mcm mice. n = 4. *P < 0.05 vs. -Tam. (H) Quantification of apoptotic cardiomyocytes shown in Fig 4I-K. n = 4. (I to K) Analysis of apoptosis in left ventricular cardiomyocytes (white arrows) in various Mdm2 and p53 mutant strains at 7 days post-Tam by immunofluorescence microscopy and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Red, anti-Mef2a. Green, TUNEL. Blue, DAPI stain of nuclear genomic DNA. (L) Induction of cell cycle entry and DNA synthesis is restricted to non-myocytes in the indicated Mdm2 and p53 mutant strains. Quantification of non-myocytes in S phase of the cell cycle shown in Fig 4M and N. n = 4. (M, N) Analysis of DNA replication in left ventricular non-myocytes (white arrows) in the indicated Mdm2 and p53 mutant strains at 7 days post-Tam by immunofluorescence microscopy. Red, anti-Mef2a. Green, BrdU. Blue, DAPI stain of nuclear genomic DNA. Mice were 13 weeks old at 14 days post-Tam (Fig 4A to C). Animals were 12 weeks old mice at 7 days post-Tam (Fig 4C to N). Abbreviations of gene names in Fig 4B: Anln, anillin actin binding protein; Apaf1, apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1; Atf3, activating transcription factor 3; Atg7, autophagy related 7; Atg4a, autophagy related 4A cysteine peptidase; Atg10, autophagy related 10; Bax, BCL2-associated X protein; Bcl6b, B cell CLL/lymphoma 6, member B; Bid, BH3 interacting domain death agonist; Birc5, baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 5; Casp1, caspase 1; Cav1, caveolae protein caveolin 1; Cd44, CD44 antigen; Cd82, CD82 antigen; Col18a1, collagen type XVIII alpha 1; Cyclin G1 (Ccng1); Dnmt1, DNA methyltransferase (cytosine-5) 1; Dram1, DNA-damage regulated autophagy modulator 1; Dusp1, dual specificity phosphatase 1; Egfr, epidermal growth factor receptor; Foxo3, forkhead box O3; Gadd45a, growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible 45 alpha; Hgf, hepatocyte growth factor; Hspa8, heat shock protein 8; Hsp90b1, heat shock protein 90 beta (Grp94) member 1; Igfbp3, insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3; Nos3, endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase 3; p21, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (Cdkn1a); Park2 (parkin), Parkinson disease autosomal recessive, juvenile 2; Pcna, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; Plk2, polo-like kinase 2; Pml, promyelocytic leukemia; pRb, retinoblastoma 1 (Rb1); Pten, PTEN induced putative kinase 1; Ras, Harvey rat sarcoma virus oncogene (Hras); Serpine1, serine (or cysteine) peptidase inhibitor clade E member 1; Tigar, Trp53 induced glycolysis regulatory phosphatase; Tnfrs1b, TNF receptor superfamily member 1B; Tpp1, tripeptidyl peptidase I; Tsc2, tuberous sclerosis 2; Ulk2, unc-51 like kinase 2; Vdr, vitamin D receptor; Zmat3, zinc finger matrin-type 3. Fig 4 data are means±s.e.m.