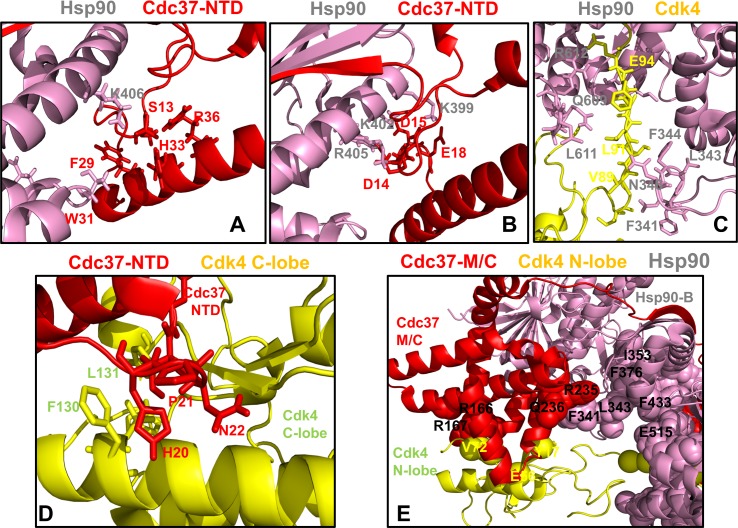
Fig 7. Structural mapping of the intermolecular interfaces and binding energy hotspots in the Hsp90-Cdc37-Cdk4 complex.
Structural analysis of the binding energy hotspots and interfaces in the chaperone-kinase complex. (A) The Hsp90 binding interface with Cdc37-NTD is centered on phosphorylated S13 (Cdc37-NTD) forming electrostatic interactions with H33, R36 and Hsp90-K406. This interface involves several other Cdc37-NTD residues (F29 and W31). (B) Another Hsp90 interfacial network with Cdc37-NTD is formed through interactions of Cdc37-NTD residues (D14, D15, E16, D17, and E18) and Hsp90-MD residues (K399, K402, R405, and K406). This binding interface features six salt bridges that stabilize the Hsp90-Cdc37 interactions. The residues are shown in colored sticks according to the domain annotation. (C) The Hsp90 interface with the Cdk4 N-lobe highlights protection of the disordered region through interactions with the Hsp90-MD Src-loop (residues F341, L343, F344) and Hsp90-CTD residues L611 and M602. (D) The Cdc37-NTD binding interface with Cdk4 C-lobe features interactions between Cdc37-NTD hotspot segment 20-HPN-22 and C-lobe αF-helix residues F130, L131. In this interface the HPN motif mimics the shape and the interaction pattern of the αC-β4 loop (Cdk4 N-lobe) with the C-lobe. (E) The Cdc37-M/C interfacial hotspots (R245, Q246, R166, and R167) are involved in binding with Hsp90 and Cdk4 proteins. The residues are shown in sticks and colored according to the domain annotation (Cdc37-NTD in red, Hsp90-B in pink, Cdk4 in yellow).