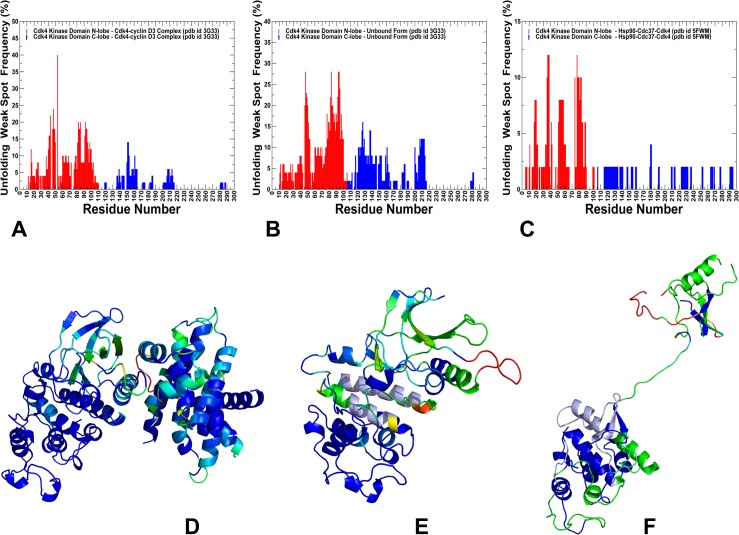
Fig 10. Rigidity decomposition analysis: Distribution of unfolding weak spots in the Cdk4 structures.
The frequency of unfolding nuclei (weak spots) in the Cdk4 catalytic domain obtained from simulations of the Cdk4-cyclin D3 complex (A), monomeric unbound form of Cdk4 (B) and Hsp90-Cdc37-Cdk4 complex (C). The frequencies of the kinase domain residues are shown in colored bars, with the N-lobe residues in red bars and C-lobe in blue bars. Unfolding nuclei or weak spots are defined as residues that break away from the giant rigid cluster immediately after transition during the network-based emulation of thermal unfolding. The higher the frequency of a weak spot, the more probable unfolding begins from these residues. Structural maps of rigidity/flexibility regions in the Cdk4 catalytic domain at the unfolding transition point obtained from emulation of thermal unfolding for the Cdk4-cyclin D3 complex (D), the monomeric unbound Cdk4 form (E) and the Hsp90-Cdc37-Cdk4 complex (F). Cdk4 conformations are colored using a color range from red (highest ranking weak spot) to blue (lowest ranking weak spot).