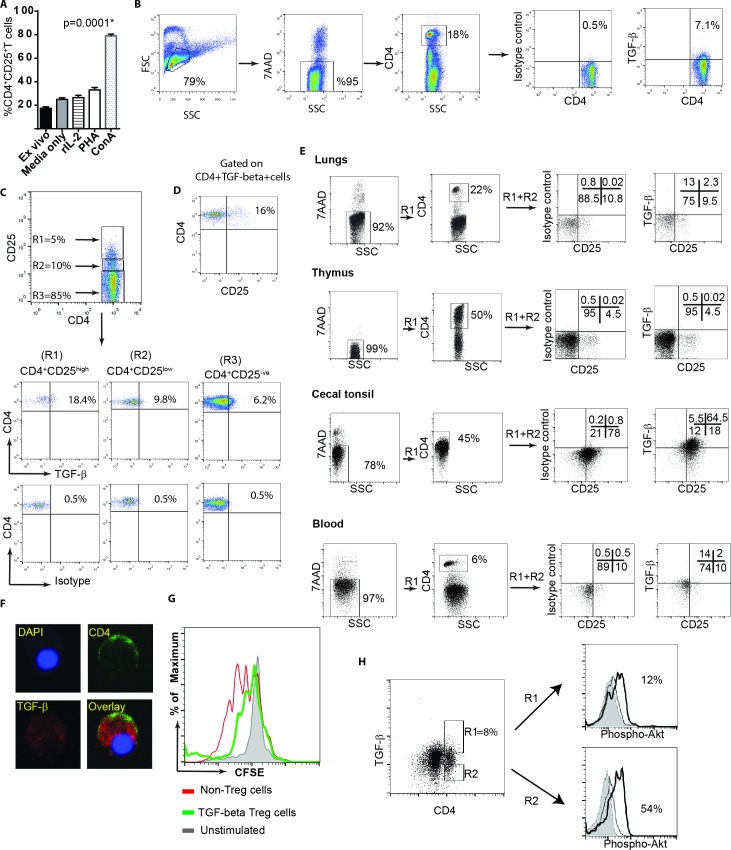
Fig 1. Identification and characterization of chicken TGF-beta+ Treg cells.
A) Mononuclear cells isolated from the spleens of 3 weeks old RIR birds were independently cultured in the presence of media only, rIL-2, PHA or Con-A at 40°C. After 72 hrs, the cells were stained with anti-CD4, and anti-CD25; 7AAD staining was used for dead cell exclusion. Data (mean ± SD) represents the percentages of CD4+CD25+ T cells in different cell culture conditions. The results are representative of three independent experiments with three biological replicates. (B) Representative FACS profiles and percentages TGF-beta+CD4+ T cells within CD4+ T cell population are shown. Mononuclear cells, isolated from spleens of 3 weeks-old naïve RIR chickens, were stained with anti-CD4-PE, anti-TGF-beta-APC mAbs and/ or isotype controls. The 7AAD was added for exclusion of dead cells. C) Representative of FACS profile and percentages TGF-beta+CD4+ T cells within three subpopulations: CD25high (R1); CD25low (R2); CD25-ve(R3) CD4+ T cells are shown. D) The percentages of CD25+ cells within TGF-beta+CD4+ T cells are shown. E) TGF-beta expressions on gated CD4+ T cells isolated from lungs, thymus, cecal tonsil, and blood of 3-weeks old RIR chickens were analysed using flow cytometry. The number in each quadrant represents percentages of the cells. The results are representative of data obtained from one out of six chickens. F) The intracellular staining of TGF-beta (Red) and cell surface CD4 (green) are shown using confocal microscopy. Mononuclear cells from spleen were stained with primary mouse anti-chicken CD4 (IgG2b), and mouse anti-TGF-beta (IgG1) monoclonal antibodies followed by staining with anti-mouse IgG1-Alexa Flur 488 or IgG2b-Alexa Flur 568 secondary antibodies, respectively. DAPI was used to visualize the nucleus. G) In vitro inhibitory function of TGF-beta+CD4+ T cells using a CFSE based proliferative assay 72 hrs after co-culture. CFSE-labelled responder cells were co-cultured with or without TGF-beta+CD4+ T cells in the presence or absence of 2.5 μg/mL Con-A. Filled grey profiles represent non-stimulated controls without co-culturing with TGF-beta+CD4+ T cells. Empty profiles represent stimulation with 2.5 μg/mL Con-A in co-culture with TGF-beta+ CD4+ T cells (green lines), or without co-culturing with TGF-β+CD4+ T cells (red lines). H) Ex vivo splenocytes isolated from RIR chickens were stimulated with PMA and stained for CD4 and TGF-beta. The levels of Phospho-AKT were analysed using Phosflow by gating on CD4+TGF-beta+ (R1) or CD4+TGF-beta- (R2) T cells. Filled grey profiles represent isotype control, thin lines represent non-activated cells, and thicker lines represent the expression of Phospho-AKT in PMA-activated cells. The percentages of cells expressing Phospho-AKT for activated cells are shown for the two sub-populations. The results represent of at least three independent experiments.