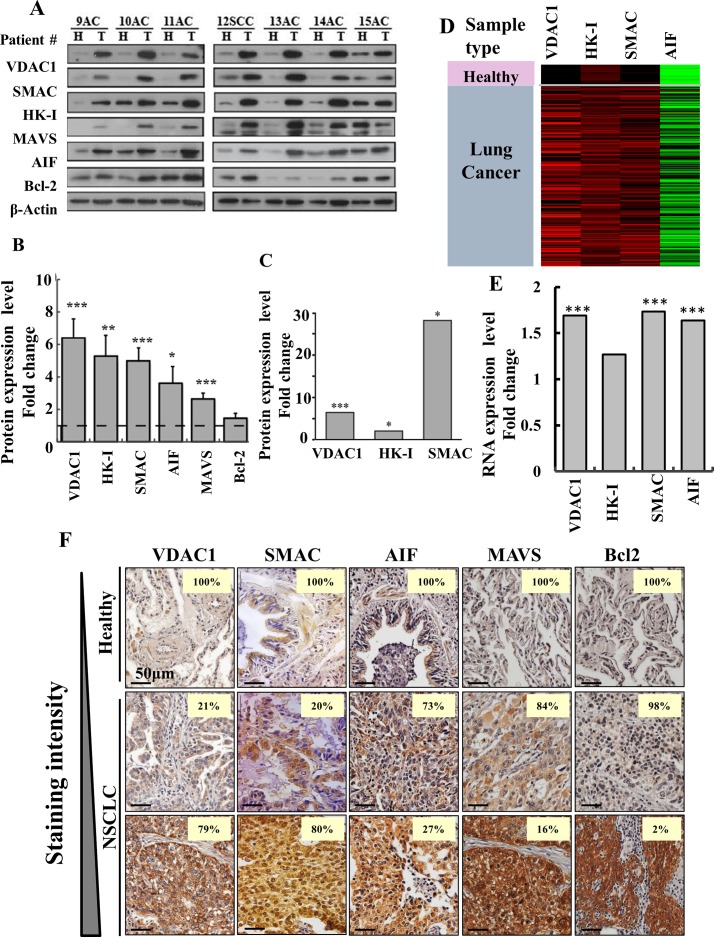
Figure 2. Over-expression of VDAC1 and other apoptosis- and energy-related proteins in lung cancer patients.
(A) Representative immunoblots of tissue lysates of tumor (T) and healthy (H) lung tissues derived from lung cancer patients probed with antibodies directed against VDAC1, SMAC, HK-I, MAVS, AIF and Bcl-2. (B) Quantitative analysis of VDAC1 (37 patients, FC=6.2, p-value=5×10−5); SMAC (37 patients, FC=5, p-value=3.4×10−5); HK-I, (33 patients, FC=5.3, p-value=5.3×10−3); MAVS (22 patients, FC=2.6, p-value=1.5×10−4); AIF (35 patients, FC=3.5, p-value=1.7×10−2), and Bcl-2 (22 patients, FC=1.5, p-value=1.4×10−1) are presented as the mean ± SD. (C) LC-HR MS/MS data for VDAC1, HK1 and SMAC. A difference between healthy and tumor tissues was considered statistically significant when P < 0.001 (***), P < 0.01 (**), P< 0.05 (*), as determined by the Mann-Whitney test for the immunoblots and a two-way t-test for the LC-HR MS/MS data. (D) Heat map showing gene expression based on RNAseq UCSC XENA data of VDAC1, HK-I, SMAC and AIF. The gene expression profiles obtained from healthy (n=110) and tumor lung samples (n=1,017) of lung cancer patients are publicly available (TCGA lung cancer dataset, detailed in Supplementary Data). (E) Quantitative analysis of the RNAseq data. (F) Over-expression of VDAC1, SMAC, AIF, MAVS and Bcl-2 in lung cancer patients. Representative IHC staining for VDAC1, SMAC AIF, MAVS and Bcl-2 of healthy (n=10) and lung cancer (n=70) tissue samples from tissue microarray slides (US Biomax). The number on each image represents the percentage of patient samples that stained at the relative intensity presented by a gradient line on the left.