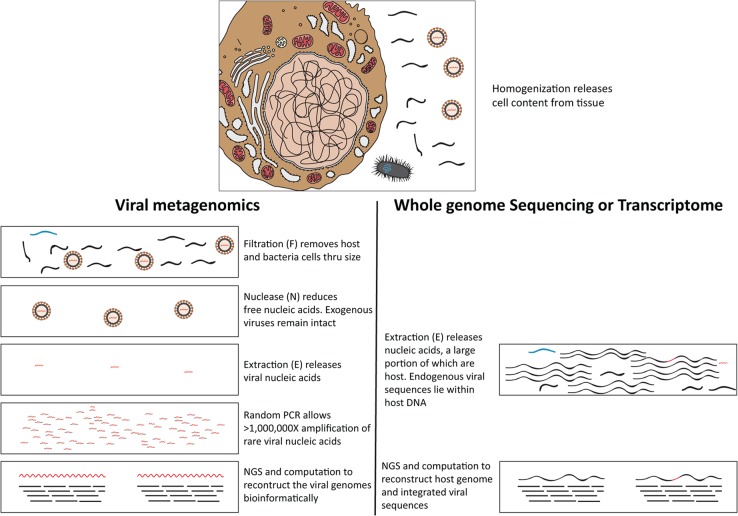
Figure 1. Schematic diagram outlines the typical viral metagenomic approach in this study, using filtration, nuclease and extraction (FNE) treatments [16, 17] to distinguish rare viral sequences from abundant host cell and free DNA.
Black wavy lines denote host nucleic acids; blue wavy lines denote bacterial nucleic acids; red wavy lines denote viral nucleic acids. In the top panel, host (Left), bacteria (bottom), and viruses (right) are schematically represented. Viral nucleic acids are protected by viral capsids from degradation during nuclease (N) treatments, unlike the host and bacterial nucleic acids. Obtaining rare exogenous viral sequence through viral metagenomics (bottom panel left) is different from obtaining endogenous viral genomes through transcriptome or whole genome sequencing (bottom panel right).