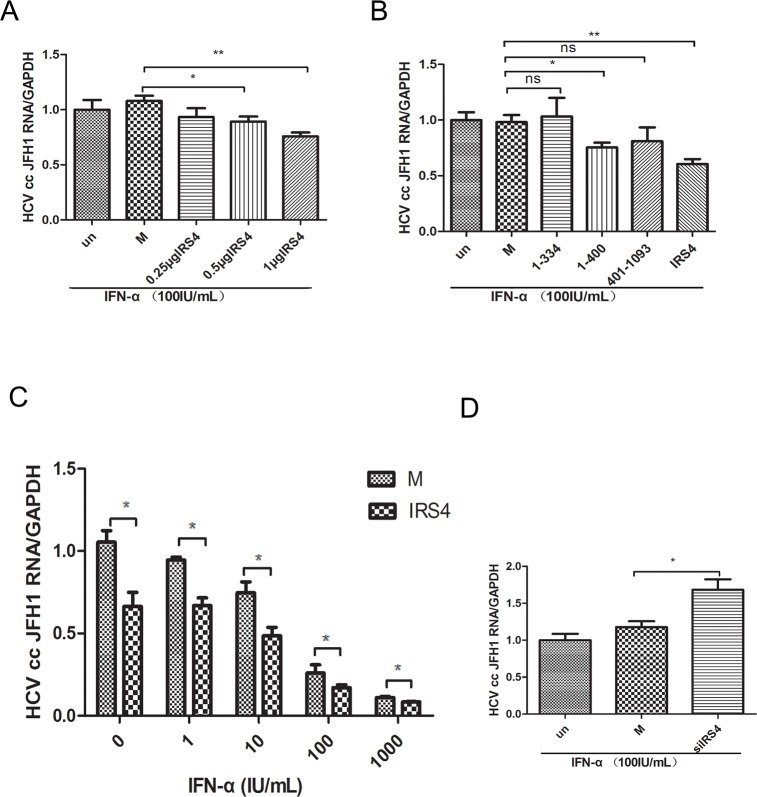
Figure 7. IRS4 regulated HCV replication in JFH1 infected Huh7.5.1 cells.
Different doses of IRS4 plasmid, Flag-tag empty plasmid (M, mock control) or nothing (un) were transfected into Huh7.5.1 cells infected with HCV JFH1. 24 hours later the cells were treated with 100IU/mL IFN-α (A) for 24 hours and the relative expression levels of HCV RNA were examined by real time PCR. (B) Two mutants IRS4 (1-334) and IRS4 (401–1093) that do not bind to USP18 have no effect on interferon anti-HCV activity. Flag empty vector (M, mock control) or IRS4 mutant 1-334 or 401-1093 were transfected into Huh7.5.1 cells infected with HCV JFH1. 24 hours later the cells were treated with 100 IU/mL IFN-α (A) for 24 hours and the relative expression levels of HCV RNA were examined by real time PCR. (C) Dosage effects of IFN-α (0, 1, 10, 100, 1000 IU/mL) on HCV replication in IRS4-overexpressed Huh7.5.1 cells infected with HCV JFH1. Relative expression levels of HCV RNA were examined by real time PCR. The values are displayed as the expression level of JFH1 HCV relative to Flag-tag empty vector (mock). Error bars indicated mean±SD, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (D) IRS4 knock-down inhibited IFN-α induced anti-HCV activity. JFH1 infected Huh7.5.1 cells were transfected with siIRS4, negative control (NC) or untreated (un), 24 hours later the cells were treated with 100 IU/mL IFN-α for 24 hours and the relative expression levels of HCV RNA were examined by real time PCR.