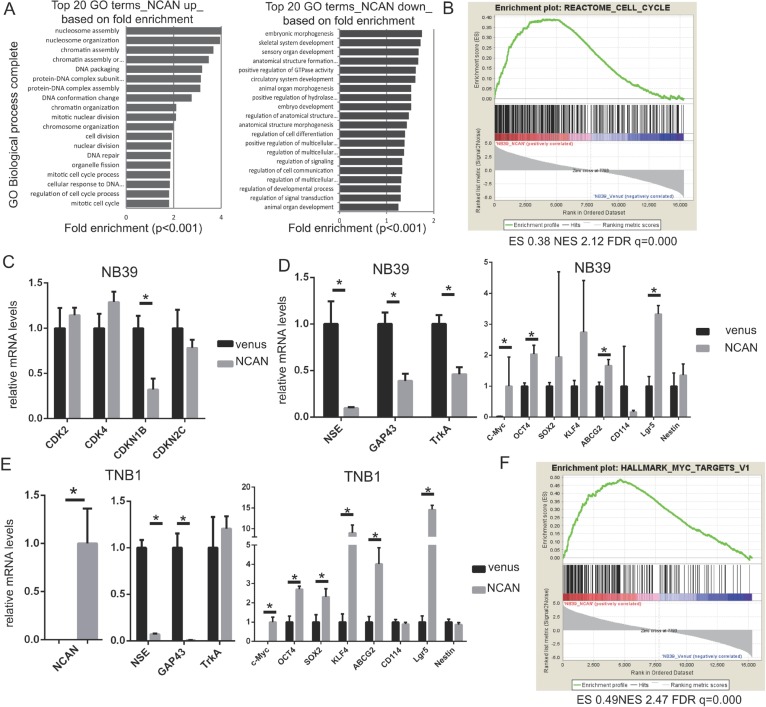
Figure 5. NCAN potentiates NB malignancy by increasing cell division and dedifferentiation.
(A) Results of the GO analysis of upregulated (left) or downregulated genes (right) in NB39 cells treated with NCAN-containing conditioned medium compared with those treated with venus-containing conditioned medium. The top 20 GO biological process terms based on fold enrichment are shown. (B) The GSEA results indicated that the gene set related to the cell cycle was significantly enriched in NB39 cells treated with NCAN-containing conditioned medium. (C) The RT-qPCR results of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and CDK inhibitors in NB39 cells treated with NCAN-containing conditioned medium compared with those treated with venus-containing conditioned medium. *p < 0.01. (D) The results of the RT-qPCR of differentiation and stemness marker genes in NB39 cells treated with NCAN-containing conditioned medium compared with those treated with venus-containing conditioned medium. *p < 0.01. (E) The RT-qPCR of the differentiation and stemness marker genes in TNB1 cells infected with NCAN-expressing or venus-expressing lentivirus. *p < 0.01. (F) The GSEA indicated that the set of MYC targets was significantly enriched in NB39 cells treated with NCAN-containing conditioned medium.