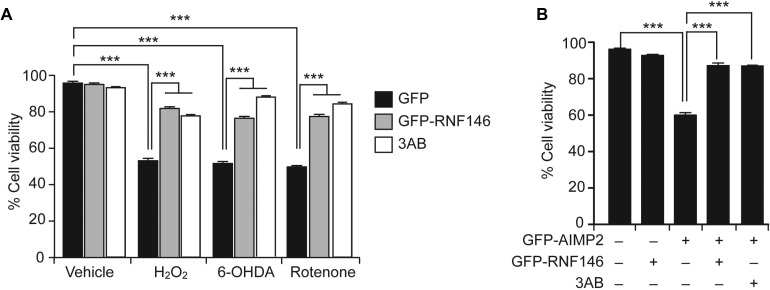
Figure 1. RNF146 expression prevents PARP-1-dependent cell death in SH-SY5Y cells.
(A) Trypan blue exclusion cell viability assay demonstrating that GFP-RNF146 expression and PARP inhibition both increase cell survival after stimulation with H2O2 (1 mM), 6-OHDA (70 uM), or rotenone (20 uM). SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with constructs driving the expression of GFP or GFP-RNF146 for 24 hrs and then treated for 24 hrs with each toxin at the indicated concentration. The PARP inhibitor 3AB (10 uM) was added to SH-SY5Y cells 4 hrs before toxin treatment (n = 6). (B) Trypan blue exclusion viability assay demonstrating that GFP-RNF146 coexpression (30 hrs) or 3AB (10 uM) treatment confers complete protection against GFP-AIMP2-mediated toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells (n = 5). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001, ANOVA test followed by Tukey post hoc analysis.