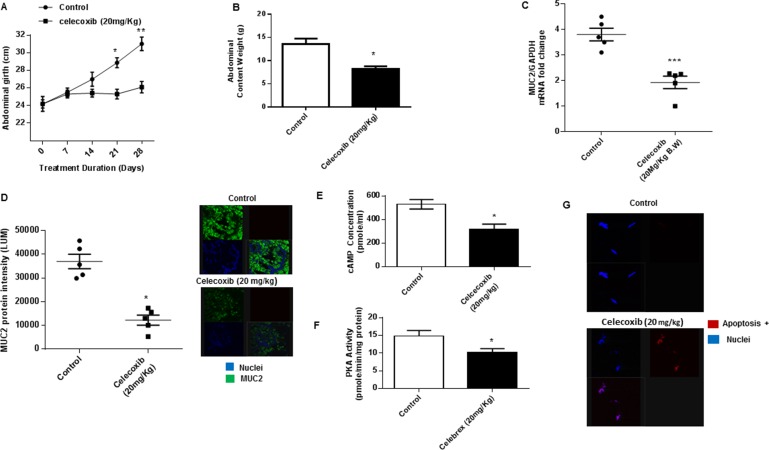
Figure 5. Celecoxib inhibits mucinous tumor growth via cAMP/PKA signaling pathway in vivo.
(A) Chronic oral gavage with celecoxib (20 mg/kg, every other day) for 28 days reduced mucinous tumor growth in our in vivo PDX model of PMP (compared to control animals treated with oral PBS gavage; 6 animals per group); serial measurements were taken of abdominal girth (mm) over the duration of treatment. (B) Intraperitoneal tumor burden (abdominal contents measured in grams) at the time of sacrifice was significantly smaller in the celecoxib-treated animals compared to control animals. Analysis of the excised tumor tissue following sacrifice demonstrated significant reduction of MUC2 mRNA expression (C) and protein expression (D); commercially available primers and probe specific for MUC2 and GAPDH cDNA were used for real-time PCR assay; relative amounts of MUC2 mRNA were determined after normalization of mucin transcripts to that of GAPDH; protein expression in tumor tissue was measured by IF staining, slides were stained with MUC2 antibody (green IF), SYTOX Orange was used to stain nucleic acid (blue IF), confocal images were randomly taken of 10 different fields (X 63 magnification) and analyzed using Image-pro Premier Software to quantify the average intensity of MUC2 protein expression. Analysis of the excised tumor tissue following sacrifice demonstrated significant reduction of cAMP concentration (E) and PKA activity (F) when compared to control mice. (G) Celecoxib significantly induced apoptosis in treated tumor tissue compared to controls; TUNEL assay was used to identify apoptotic cells. (Figure 5G) Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM) from triplicate experiments. Asterisk represents a statistically significant difference compared with the control group (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). (PMP: pseudomyxoma peritonei; PCR: polymerase chain reaction; IF: immunofluorescence).