Figure 1: Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Versus Control on Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Twenty Four Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea.
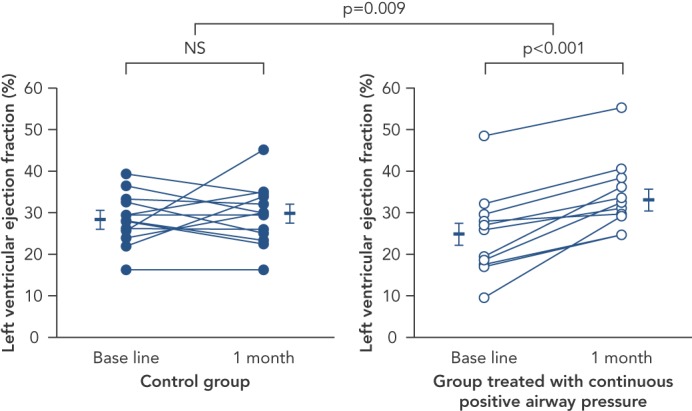
A statistically-significant increase in ejection fraction is noted with CPAP treatment as compared to control (p=0.009) (absolute increase in EF of 8.8 ± 1.6 %, relative increase in EF of 35 % [p<0.001]). CPAP = continuous positive airway pressure; EF = ejection fraction; NS = not significant. Source: Kaneko, et al., 2003, published with permission.44.
