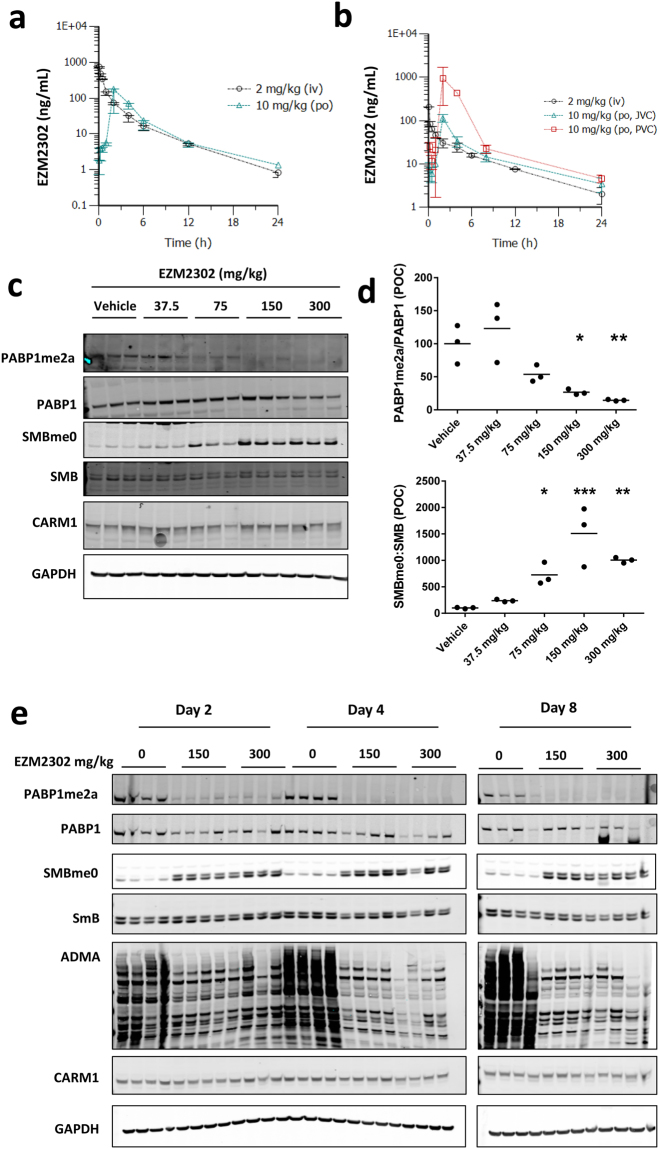
Figure 4.
EZM2302 is orally available with potent in vivo CARM1 inhibition. (a) Preclinical PK of EZM2302 in (a), CD-1 mouse and (b) Sprague-Dawley rat with or without jugular- and portal-vein cannulation (JVC and PVC). Data are shown graphically as plasma concentration vs. time profile of mean ± SD (n = 3) following i.v. bolus or oral gavage administration. (c) Methyl mark changes induced by twice daily (BID) administration of EZM2302 for 7 days at 150 and 300 mg/kg in untumored CB-17 SCID mice. Compound administration was stopped on day 7, and liver tissue was harvested for PD analysis. (d) Each point represents the ratio of PABP1me2a to PAPB1 or SmBme0 to SmB normalized to the vehicle control, measured by western blot. The horizontal lines represent group mean values. Dose groups that showed a statistically significant inhibition are indicated (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, versus vehicle, 1-way ANOVA with a Dunnett’s post-test) P values compared to vehicle were: PABP1me2a: 37.5 mg/kg p = 0.634, 75 mg/kg p = 0.137, 150 mg/kg p = 0.016, 300 mg/kg p = 0.006, SMBme0: 37.5 mg/kg p = 0.092, 75 mg/kg p = 0.052, 150 mg/kg p = 0.0003, 300 mg/kg p = 0.007. (e) CARM1 target inhibition in RPMI-8226 xenograft tumor tissue collected from mice euthanized after 2, 4, and 8 days of BID dosing at 150 and 300 mg/kg EZM2302. Images in C and E have been cropped. Uncropped images are presented in Supplementary Figs S9 and S10.