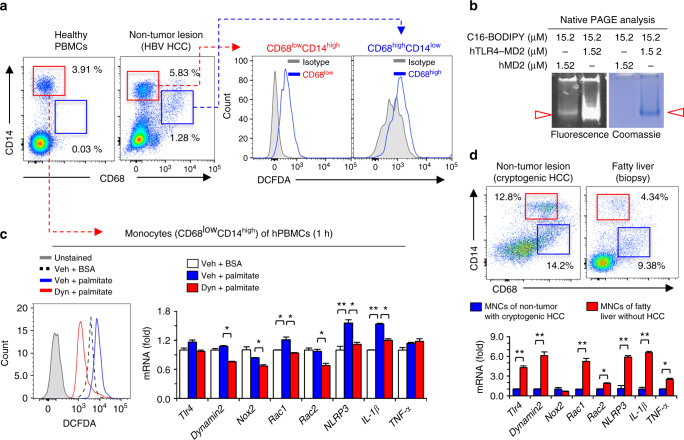
Fig. 7. Palmitate treatment increases ROS generation in human CD68lowCD14high monocytes via endocytosis of palmitate/TLR4 complex.
a Healthy human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and isolated liver mononuclear cells (MNCs) from non-tumor lesions of HCC (HBV origin) were subjected to flow cytometry and assessment of ROS generation, respectively. b After the reaction between each protein and BODIPY-labeled fluorescent fatty acid analog (C16-BODIPY) under the indicated conditions, the samples loaded at Native gradient PAGE (4–15%) were visualized with illumination (488 nm) and Coomassie staining. c Healthy human PBMCs were treated with palmitate ± dynasore. Then, these cells were subjected to assessment of ROS generation and qRT–PCR analyses. d Freshly isolated liver MNCs from non-tumor liver lesions of primary HCC and biopsy lesions of fatty liver were subjected to flow cytometry and qRT–PCR analyses. Data are representative of three independent experiments using PBMC of healthy controls (n = 5) and liver MNCs of HBV (n = 3), cryptogenic HCC (n = 1) and fatty liver (n = 1) patients a, c, d. Data are expressed as the mean ± s.e.m. and analyzed by Student’s t-test or one-way analysis of variance, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 in comparison with the corresponding controls