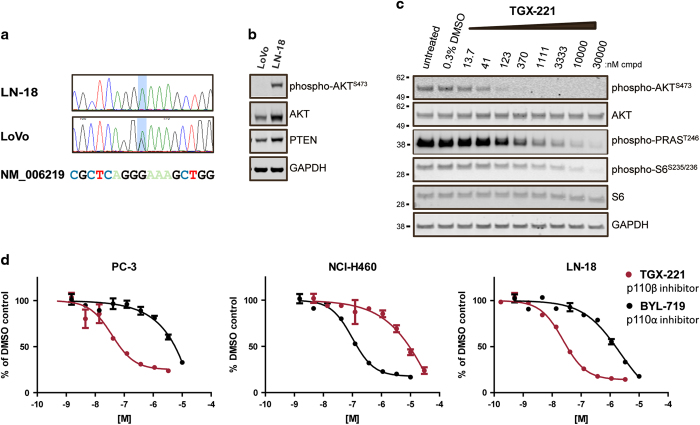
Figure 3.
PI3K signaling in cells with an endogenous PIK3CB mutation is dependent on p110β. (a) Sequence of PIK3CB in LN-18 and LoVo cell gDNA identified 2 missense mutations at the same codon located within the kinase domain. Light blue shading indicates the location of the nucleotide change. (b) Immunoblot of lysates of LoVo and LN-18 cells cultured overnight in media containing 10% fetal bovine serum probed using antibodies to detect the level of p-AKT, AKT, PTEN and GAPDH expression. A total of 20 μg of protein was loaded in each lane. (c) Immunoblot of lysates of LN-18 cells treated with cell culture media containing 0.3% DMSO or TGX-221 at indicated concentration in 0.3% DMSO were probed using antibodies to detect inhibition of p-AKT, p-PRAS40 and p-S6. (d) p-AKT ELISA in PC-3 (PTEN null, p110αwt, and p110βwt), LN-18 (PTENwt, p110αwt, and p110βE1051K) and NCI-H460 cells (PTENwt, p110αE545K, and p110βwt). Cells were treated with TGX-221 or BYL-719 in DMSO or DMSO alone for 2 h and lysed, and the lysates were probed with antibodies to detect AKT or phospho-AKTS473 using a multiplex electrochemiluminescent ELISA assay. RLU signal was quantified using an MSD SI2400. p-AKT signal was normalized to total AKT (expressed as % p-AKT) and then indexed to DMSO treated cells. Shown are dose response curves that are representative examples of replicates from individual experiments (error bars indicate standard deviation of duplicate samples; where they are not clearly visible, the error in the replicates is too low to be seen on the plot). Mean data of duplicate samples from two independent experiments are listed in Table 3.