Figure 1.
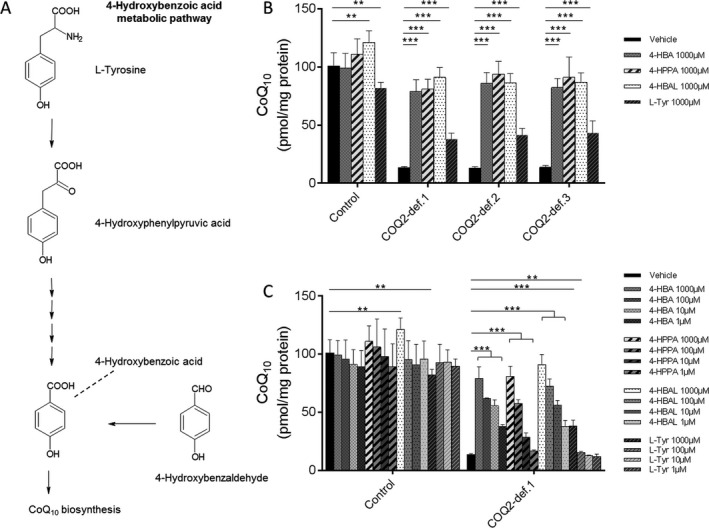
4‐hydroxybenzoic acid (4‐HBA) metabolic pathway and effects of 4‐HBA on CoQ10 biosynthesis in human COQ2 deficiency. (A) Schematic illustration of the 4‐hydroxybenzoic acid (4‐HBA) metabolic pathway in human cells. (B) Quantitative analysis of CoQ10 levels in control and COQ2 deficient fibroblast cell lines measured by UPLC‐MS/MS. For details regarding the cell lines COQ2‐def.1, COQ2‐def.2 and COQ2‐def.3 see Table S1. The different cell lines were treated with 4‐hydroxybenzoic acid (4‐HBA), 4‐hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid (4‐HPPA), 4‐hydroxybenzaldehyde (4‐HBAL), and L‐tyrosin (L‐Tyr), respectively. The effect of each concentration was expressed relative to values obtained with vehicle‐treated control cells, which was set at 100%, measured on the same day. (C) Quantitative analysis of CoQ10 levels in control and COQ2‐def.1 fibroblast using different concentrations of 4‐HBA, 4‐HPPA, 4‐HBAL and L‐Tyr. Statistics: ***P < 0.001) and **P < 0.01) relative to the indicated condition. Statistical significance was assessed using Student's t‐test. All experimental data was obtained in at least three independent experiments.
