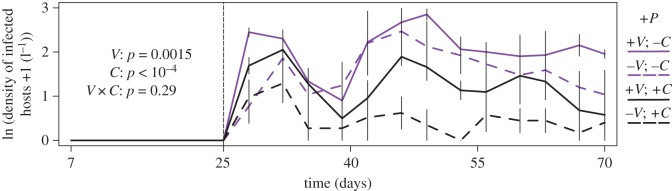
Figure 5.
Infections and Dilution Effect: The density of infected hosts is lowered by competitors/diluters but elevated by higher standing trait variation. Diluters reduce the integrated density of infected hosts at both levels of trait variability (C effect; black versus purple lines). However, higher standing trait variation allows the rapid evolution of enhanced competitive ability (driven especially by parasites; figure 3). In turn, higher competitive ability buffers total densities of focal hosts from competition and disease (figure 4). Consequently, these higher total densities lead to a higher density of infected hosts (V effect; solid versus dashed lines). Presence of competitors/diluters and trait variability do not interact (no C × V interaction). Thus, rapid evolution does not undermine the dilution effect. Abbreviations: V = standing trait variation; C = competitors/diluters. Error bars are standard errors.