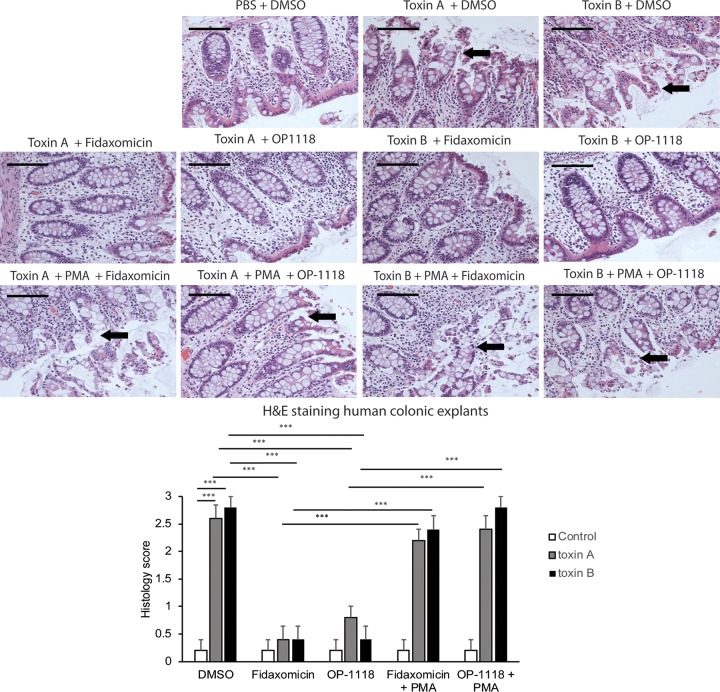
FIG 5.
Fidaxomicin inhibits toxin A- and B-mediated epithelial cell damage in fresh human colonic explants via NF-κB inhibition. (Top) The histological structure of the treated human colonic tissues was evaluated by H&E staining at a ×200 magnification. Luminal epithelial cell linings were damaged in human colonic explants exposed to toxin A or toxin B. Arrows indicate the locations of epithelial damage. Black bars, 100 μm. (Bottom) Histology scores for human colonic explants. C. difficile toxins caused damage to the colonic mucosal epithelial layer. The data are pooled from 6 patients per group. ***, P < 0.001.