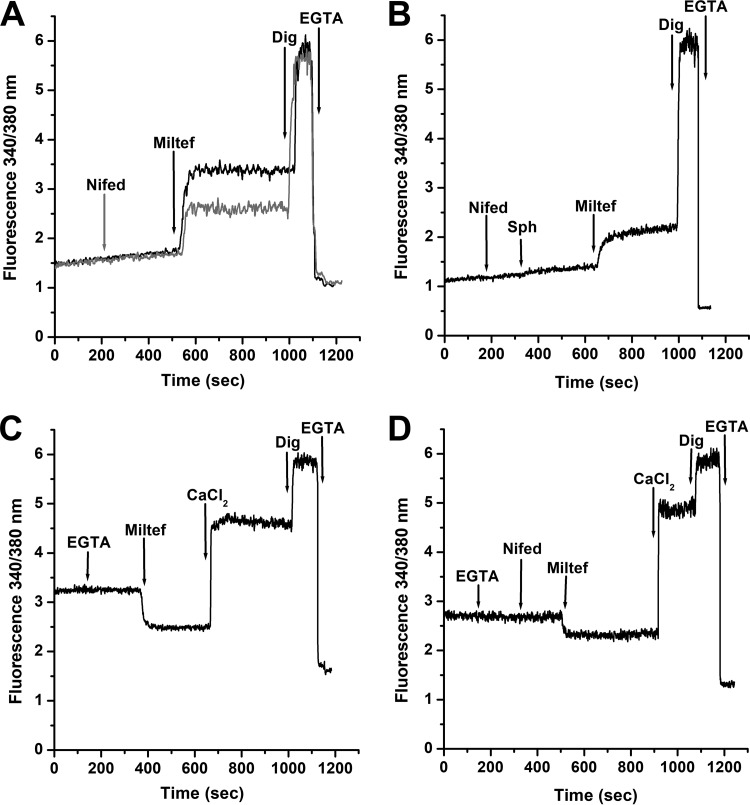
FIG 3.
Effect of the L-type VGCC channel blocker nifedipine on the action of miltefosine on the intracellular Ca2+ concentration of L. donovani promastigotes. (A) Black line indicates effects of miltefosine (4 μM) in the presence of extracellular CaCl2 (2 mM), followed by digitonin (40 μM) and EGTA (arrows), respectively. Gray line indicates effects of nifedipine (4 μM), followed by miltefosine (4 μM) in the presence of 2 mM extracellular Ca2+, followed by digitonin (40 μM) and EGTA (arrows), respectively. (B) Effect of nifedipine (4 μM) followed by sphingosine (10 μM), miltefosine (4 μM), digitonin (40 μM) and EGTA, respectively (arrows) in the presence of 2 mM extracellular Ca2+. (C) Effect of miltefosine in the absence of extracellular Ca2+. EGTA was added to chelate any contaminating extracellular Ca2+ (arrow), followed by miltefosine (4 μM), CaCl2 (2 mM), digitonin (40 μM), and EGTA, respectively. (D) Effect of miltefosine after addition of nifedipine in the absence of extracellular Ca2+. EGTA was added to chelate any contaminating extracellular Ca2+ (arrow), followed by nifedipine (4 μM), miltefosine (4 μM), CaCl2 (2 mM), digitonin (40 μM), and EGTA, respectively. Traces are representative of at least three independent experiments.