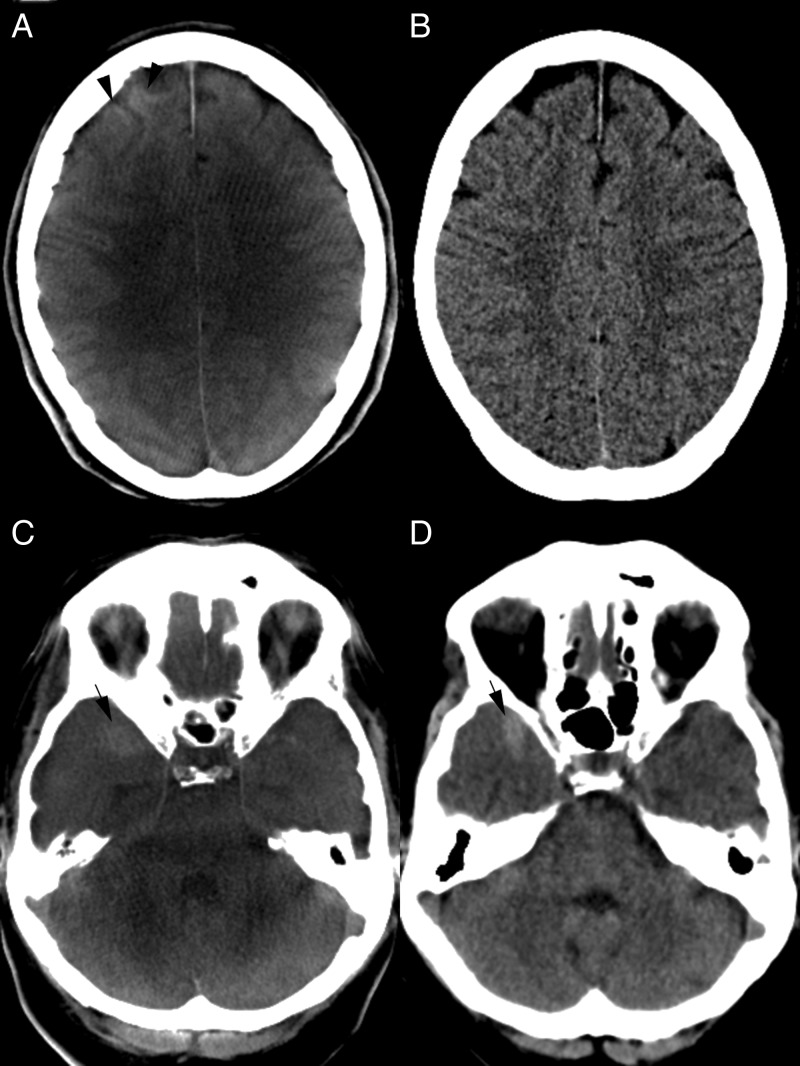
Figure 1.
(A, B) CT images after balloon assisted coil embolization of an anterior communicating artery aneurysm. (A) Flat detector CT (FDCT) shows a cortical hyperattenuation of the right frontal lobe (black arrowhead). A subarachnoidal hemorrhage (SAH) can be excluded on both FDCT (A) and follow-up multidetector CT (MDCT) (B) images. Gray–white matter differentiation as well as exclusion of postinterventional ischemic lesions is feasible in both examinations. (C, D) Right temporal SAH. Blood is delineated on both FDCT (C) and MDCT (D) examinations (black arrows). Gray–white matter differentiation of the cerebellum is limited on FDCT (C) but the fourth ventricle is clearly depicted and an intraventricular hemorrhage can be excluded.