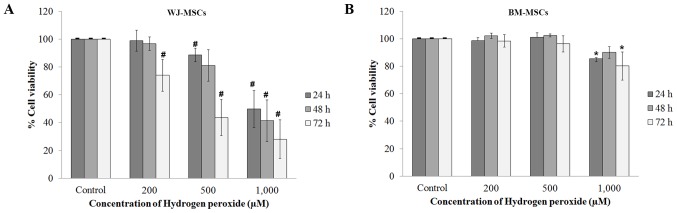
Figure 2.
The viability was evaluated in MSCs treated with H2O2 alone comparison with the control (no H2O2 treatment). MSCs were treated with H2O2 (200, 500 or 1,000 µM) at 24, 48 and 72 h. (A) The viability of WJ-MSCs relative to that of the control cells was reduced by H2O2 treatment in a dose-dependent manner. (B) The viability of BM-MSCs differed from that of control cells only after treatment with 1,000 µM H2O2. Values are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean of six separate experiments performed in triplicate in WJ-MSCs and three separate experiments performed in triplicate in BM-MSCs. #,*P<0.05 vs. control group for WJ-MSCs or BM-MSCs, respectively. BM-MSCs, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; WJ-MSCs, Wharton's jelly-derived MSCs.