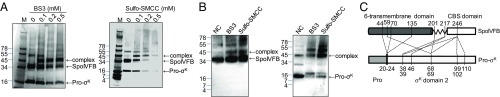
Fig. 4.
Cross-linking of a SpoIVFB–Pro-σK complex. (A) SDS/PAGE after chemical cross-linking. The purified complex was incubated with the indicated cross-linkers at the indicated concentrations, or with no cross-linker as a control, and samples including protein markers (M, molecular mass in kilodaltons at Left) were subjected to SDS/PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. Position of 1:1 complex of SpoIVFB and Pro-σK is indicated. (B) Immunoblot analysis after chemical cross-linking. The purified complex was incubated with the indicated cross-linkers at 0.1 mM, or with no cross-linker (NC) as a control, and samples were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-FLAG (Left) or anti-His (Right) antibodies to detect SpoIVFB or Pro-σK, respectively. Positions of protein markers and 1:1 complex of SpoIVFB and Pro-σK are indicated. (C) Summary of interchain cross-links used in modeling. Cys substitutions for residues 44, 70, and 135 of SpoIVFB formed disulfide cross-links with Cys substitutions for some of the residues spanning from at least residues 20–24 of Pro-σK (25). The other dashed lines depict the chemical cross-links listed in SI Appendix, Table S2. Pro-σK(1-127), including the Prosequence (1–21) and σK domain 2 (22-127), is depicted (on a different scale than SpoIVFB) since Pro-σK(1-127) was used in all of the cross-linking experiments.