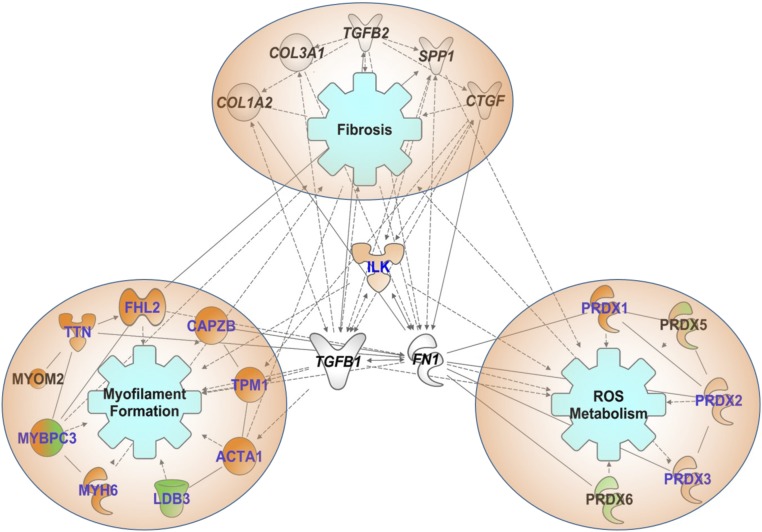
Fig. 7.
Bioinformatics analysis provided plausible associations between selected SNO proteins and fibrosis pathways. Proteins that showed SNO change in dmdmdx:utrn+/− were analyzed. Filled shapes indicated the following: proteins where a (or most of the) site(s) was/were hyper-SNO in dmdmdx:utrn+/− (dark orange); proteins where a (or most of the) site(s) was/were hypo-SNO in dmdmdx:utrn+/− (dark green); hyper-SNO or hypo-SNO, but the change did not exceed the average coefficient of variation (light orange or light green); some sites were hyper-SNO and others were hypo-SNO on that protein (mixed orange/green); fibrosis markers confirmed in the level of transcriptome (no filling). Letters in blue indicate SNO on (a) site(s) of the protein was/were reversed with Trpc6-deletion. Of the enriched functional categories, networks of myofilament proteins, multiple isoforms of Prdxs and ILK were selected as being of particular interest. In addition, based on our study on fibrosis, fibrotic markers were included for internetwork generation. Proteins where this network analysis provided the associations between the SNO genes that might affect fibrosis pathways directly/indirectly in DMD pathophysiology are shown.