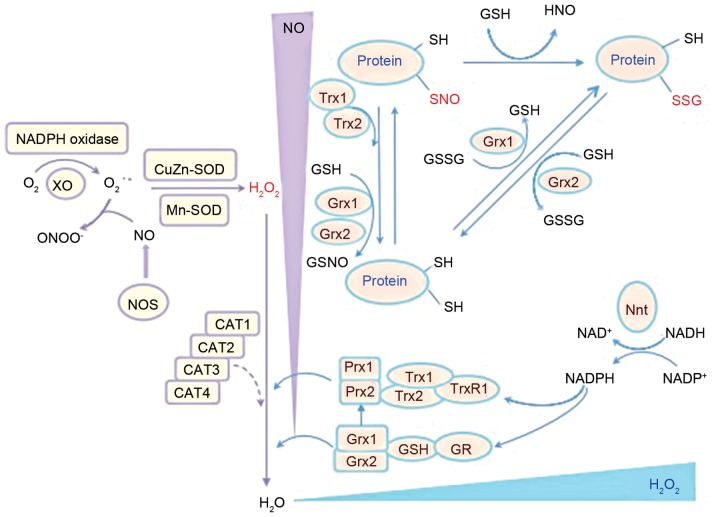
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the antioxidant chain of C. neoformans and the primary antioxidant enzymes involved. Prx, Trx and Grx systems are major enzymatic antioxidant systems in C. neoformans that regulate redox balance (49–51) that are associated with 2 SODs, Cu/Zn-SOD (SOD1) and Mn-SOD (SOD2), which may convert superoxide to hydrogen peroxide (61). C. neoformans, Cryptococcus neoformans; CAT, catalase; GR, glutathione reductase; Grx, glutaredoxin; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, glutathione disulfide; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; Nnt, nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase; NO, nitric oxide; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; protein-SNO, protein nitrosylation; protein-SSG, protein glutathionylation; Prx1/2, peroxiredoxin 1/2; SH, thiol; SOD, superoxide dismutase; Trx, thioredoxin; TrxR, thioredoxin reductase.